Efficient oncogene silencing and metastasis inhibition via systemic delivery of siRNA
- PMID: 18388916
- PMCID: PMC2778045
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2008.51
Efficient oncogene silencing and metastasis inhibition via systemic delivery of siRNA
Abstract
The selective delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) to metastatic tumors remains a challenging task. We have developed a nanoparticle (NP) formulation composed of siRNA, a carrier DNA, a polycationic peptide, and cationic liposomes. The NP was obtained by a self-assembling process, followed by surface modification with a polyethylene glycol (PEG)-conjugated ligand, anisamide. The NP was PEGylated and a ligand was presented to target sigma receptor-expressing murine melanoma cells, B16F10. The lung metastasis model was established by intravenous (i.v.) injection of the B16F10 cells into C57BL/6 mice. A mixture of siRNA against MDM2, c-myc, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) co-formulated in the targeted NP caused simultaneous silencing of each of the oncogenes in the metastatic nodules. Two consecutive i.v. injections of siRNA in the targeted NP significantly reduced the lung metastasis (approximately 70-80%) at a relatively low dose (0.45 mg/kg), whereas free siRNA and the nontargeted NP showed little effect. This targeted NP formulation significantly prolonged the mean survival time of the animals by 30% as compared to the untreated controls. At the therapeutic dose, the targeted NP showed little local and systemic immunotoxicity and did not decrease the body weight or damage the major organs.
Figures

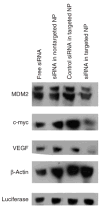
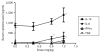
References
-
- Geschwind JF, Dagli MS, Vogel-Claussen J, Seifter E, Huncharek MS. Metastatic breast carcinoma presenting as a large pulmonary embolus: case report and review of the literature. Am J Clin Oncol. 2003;26:89–91. - PubMed
-
- Ashley AC, Deschamps C, Alberts SR. Impact of prognostic factors on clinical outcome after resection of colorectal pulmonary metastases. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2006;6:32–37. - PubMed
-
- Bacci G, Avella M, Picci P, Briccoli A, Dallari D, Campanacci M. Metastatic patterns in osteosarcoma. Tumori. 1988;74:421–427. - PubMed
-
- Murakami T, Cardones AR, Hwang ST. Chemokine receptors and melanoma metastasis. J Dermatol Sci. 2004;36:71–78. - PubMed
-
- Jana S, Chakraborty C, Nandi S, Deb JK. RNA interference: potential therapeutic targets. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004;65:649–657. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

