The interferon response inhibits HIV particle production by induction of TRIM22
- PMID: 18389079
- PMCID: PMC2279259
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000007
The interferon response inhibits HIV particle production by induction of TRIM22
Abstract
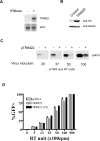
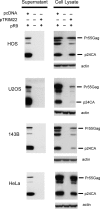
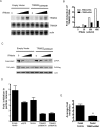
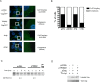
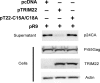
Treatment of human cells with Type 1 interferons restricts HIV replication. Here we report that the tripartite motif protein TRIM22 is a key mediator. We used transcriptional profiling to identify cellular genes that were induced by interferon treatment and identified TRIM22 as one of the most strongly up-regulated genes. We confirmed, as in previous studies, that TRIM22 over-expression inhibited HIV replication. To assess the role of TRIM22 expressed under natural inducing conditions, we compared the effects of interferon in cells depleted for TRIM22 using RNAi and found that HIV particle release was significantly increased in the knockdown, implying that TRIM22 acts as a natural antiviral effector. Further studies showed that TRIM22 inhibited budding of virus-like particles containing Gag only, indicating that Gag was the target of TRIM22. TRIM22 did not block the release of MLV or EIAV Gag particles. Inhibition was associated with diffuse cytoplasmic staining of HIV Gag rather than accumulation at the plasma membrane, suggesting TRIM22 disrupts proper trafficking. Mutational analyses of TRIM22 showed that the catalytic amino acids Cys15 and Cys18 of the RING domain are required for TRIM22 antiviral activity. These data disclose a pathway by which Type 1 interferons obstruct HIV replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Sen GC. Viruses and interferons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001;55:255–281. - PubMed
-
- Karpov AV. Endogenous and exogenous interferons in HIV-infection. Eur J Med Res. 2001;6:507–524. - PubMed
-
- Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BRG, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD. How Cells Respond to Interferons. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227–264. - PubMed
-
- Agy MB, Acker RL, Sherbert CH, Katze MG. Interferon treatment inhibits virus replication in HIV-1 and SIV-infected CD4+ T-cell lines by distinct mechanisms: evidence for decreased stability and aberrant processing of HIV-1 proteins. Virology. 1995;214:379–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

