Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers
- PMID: 18390968
- PMCID: PMC2718422
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4956
Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PKs), and pharmacodynamics (PDs) of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancer.
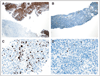
Patients and methods: In part A, patients received escalating doses to determine the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD). In both parts, blood samples were collected to assess PK and PD parameters. In part B, patients were stratified by cancer type (melanoma v other) and randomly assigned to receive the MTD or 50% MTD. Biopsies were collected to determine inhibition of ERK phosphorylation, Ki-67 expression, and BRAF, KRAS, and NRAS mutations.
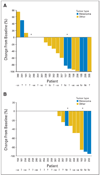
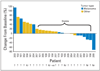
Results: Fifty-seven patients were enrolled. MTD in part A was 200 mg bid, but this dose was discontinued in part B because of toxicity. The 50% MTD (100 mg bid) was well tolerated. Rash was the most frequent and dose-limiting toxicity. Most other adverse events were grade 1 or 2. The PKs were less than dose proportional, with a median half-life of approximately 8 hours and inhibition of ERK phosphorylation in peripheral-blood mononuclear cells at all dose levels. Paired tumor biopsies demonstrated reduced ERK phosphorylation (geometric mean, 79%). Five of 20 patients demonstrated >or= 50% inhibition of Ki-67 expression, and RAF or RAS mutations were detected in 10 of 26 assessable tumor samples. Nine patients had stable disease (SD) for >or= 5 months, including two patients with SD for 19 (thyroid cancer) and 22 (uveal melanoma plus renal cancer) 28-day cycles.
Conclusion: AZD6244 was well tolerated with target inhibition demonstrated at the recommended phase II dose. PK analyses supported twice-daily dosing. Prolonged SD was seen in a variety of advanced cancers. Phase II studies are ongoing.
Conflict of interest statement
Although all authors completed the disclosure declaration, the following author(s) indicated a financial or other interest that is relevant to the subject matter under consideration in this article. Certain relationships marked with a “U” are those for which no compensation was received; those relationships marked with a “C” were compensated. For a detailed description of the disclosure categories, or for more information about ASCO’s conflict of interest policy, please refer to the Author Disclosure Declaration and the Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest section in Information for Contributors.
Figures
References
-
- Sebolt-Leopold JS, Dudley DT, Herrera R, et al. Blockade of the MAP kinase pathway suppresses growth of colon tumors in vivo. Nat Med. 1999;5:810–816. - PubMed
-
- Tecle H. The development of kinase inhibitors with unusual mechanism of action: CI-1040, a selective, non-ATP competitive MEK inhibitor in the clinic. Presented at the IBC 2nd International Conference of Protein Kinases: Target Validation, Drug Discovery and Clinical Development of Kinase Therapeutics; September 9–10, 2002; Boston, MA.
-
- Trachet E, Przybranowski S, Howard C. In vivo evaluation of MEK inhibitor, CI-1040 (PD 0184352), against a panel of human pancreatic tumor xenografts. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2002;43:2096. (abstr 5426)
-
- Yeh TC, Marsh V, Bernat BA, et al. Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent, highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1576–1583. - PubMed
-
- Huynh H, Soo KC, Chow PK, et al. Targeted inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase pathway with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:138–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

