Either a Th17 or a Th1 effector response can drive autoimmunity: conditions of disease induction affect dominant effector category
- PMID: 18391061
- PMCID: PMC2292220
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20071258
Either a Th17 or a Th1 effector response can drive autoimmunity: conditions of disease induction affect dominant effector category
Abstract
Experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) represents autoimmune uveitis in humans. We examined the role of the interleukin (IL)-23-IL-17 and IL-12-T helper cell (Th)1 pathways in the pathogenesis of EAU. IL-23 but not IL-12 was necessary to elicit disease by immunization with the retinal antigen (Ag) interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) in complete Freund's adjuvant. IL-17 played a dominant role in this model; its neutralization prevented or reversed disease, and Th17 effector cells induced EAU in the absence of interferon (IFN)-gamma. In a transfer model, however, a polarized Th1 line could induce severe EAU independently of host IL-17. Furthermore, induction of EAU with IRBP-pulsed mature dendritic cells required generation of an IFN-gamma-producing effector response, and an IL-17 response by itself was insufficient to elicit pathology. Finally, genetic deficiency of IL-17 did not abrogate EAU susceptibility. Thus, autoimmune pathology can develop in the context of either a Th17 or a Th1 effector response depending on the model. The data suggest that the dominant effector phenotype may be determined at least in part by conditions present during initial exposure to Ag, including the quality/quantity of Toll-like receptor stimulation and/or type of Ag-presenting cells. These data also raise the possibility that the nonredundant requirement for IL-23 in EAU may extend beyond its role in promoting the Th17 effector response and help provide a balance in the current Th1 versus Th17 paradigm.
Figures
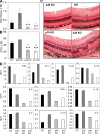
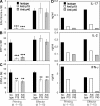
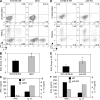


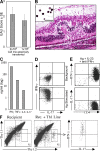



Comment in
-
A rush to judgment on Th17.J Exp Med. 2008 Jul 7;205(7):1517-22. doi: 10.1084/jem.20072066. J Exp Med. 2008. PMID: 18591407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oppmann, B., R. Lesley, B. Blom, J.C. Timans, Y. Xu, B. Hunte, F. Vega, N. Yu, J. Wang, K. Singh, et al. 2000. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 13:715–725. - PubMed
-
- Gregerson, D.S., W.F. Obritsch, S.P. Fling, and J.D. Cameron. 1986. S-antigen-specific rat T cell lines recognize peptide fragments of S-antigen and mediate experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis and pinealitis. J. Immunol. 136:2875–2882. - PubMed
-
- Caspi, R.R., F.G. Roberge, C.G. McAllister, M. el-Saied, T. Kuwabara, I. Gery, E. Hanna, and R.B. Nussenblatt. 1986. T cell lines mediating experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) in the rat. J. Immunol. 136:928–933. - PubMed
-
- Mochizuki, M., T. Kuwabara, C. McAllister, R.B. Nussenblatt, and I. Gery. 1985. Adoptive transfer of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in rats. Immunopathogenic mechanisms and histologic features. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 26:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal, R.K., and R.R. Caspi. 2004. Rodent models of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Methods Mol. Med. 102:395–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

