Decreased corticolimbic allopregnanolone expression during social isolation enhances contextual fear: A model relevant for posttraumatic stress disorder
- PMID: 18391192
- PMCID: PMC2291140
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0801853105
Decreased corticolimbic allopregnanolone expression during social isolation enhances contextual fear: A model relevant for posttraumatic stress disorder
Abstract
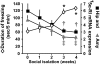
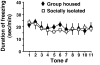
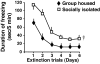
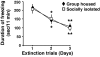
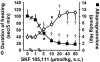
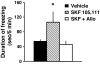
Mice subjected to social isolation (3-4 weeks) exhibit enhanced contextual fear responses and impaired fear extinction. These responses are time-related to a decrease of 5alpha-reductase type I (5alpha-RI) mRNA expression and allopregnanolone (Allo) levels in selected neurons of the medial prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala. Of note, the cued fear response was not different between group housed and socially isolated mice. In socially isolated mice, S-norfluoxetine, a selective brain steroidogenic stimulant (SBSS), in doses (0.45-1.8 mumol/kg) that increase brain Allo levels but fail to inhibit serotonin reuptake, greatly attenuates enhanced contextual fear response. SKF 105,111 (a potent 5alpha-RI inhibitor) decreases corticolimbic Allo levels and enhances the contextual fear response in group housed mice, which suggests that social isolation alters emotional responses by reducing the positive allosteric modulation of Allo at GABA(A) receptors in corticolimbic circuits. Thus, these procedures model emotional hyperreactivity, including enhanced contextual fear and impaired contextual fear extinction, which also is observed in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) patients. A recent clinical study reported that cerebrospinal fluid Allo levels also are down-regulated in PTSD patients and correlate negatively with PTSD symptoms and negative mood. Thus, protracted social isolation of mice combined with tests of fear conditioning may be a suitable model to study emotional behavioral components associated with neurochemical alterations relating to PTSD. Importantly, drugs like SBSSs, which rapidly increase corticolimbic Allo levels, normalize the exaggerated contextual fear responses resulting from social isolation, suggesting that selective activation of neurosteroidogenesis may be useful in PTSD therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
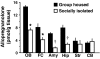
Similar articles
-
Neurosteroid biosynthesis regulates sexually dimorphic fear and aggressive behavior in mice.Neurochem Res. 2008 Oct;33(10):1990-2007. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9718-5. Epub 2008 May 13. Neurochem Res. 2008. PMID: 18473173 Review.
-
In a mouse model relevant for post-traumatic stress disorder, selective brain steroidogenic stimulants (SBSS) improve behavioral deficits by normalizing allopregnanolone biosynthesis.Behav Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;21(5-6):438-50. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32833d8ba0. Behav Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20716970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S-norfluoxetine microinfused into the basolateral amygdala increases allopregnanolone levels and reduces aggression in socially isolated mice.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Jun;60(7-8):1154-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.10.011. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 20971127 Free PMC article.
-
SSRIs act as selective brain steroidogenic stimulants (SBSSs) at low doses that are inactive on 5-HT reuptake.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;9(1):24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2008.12.006. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19157982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ganaxolone improves behavioral deficits in a mouse model of post-traumatic stress disorder.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Sep 11;8:256. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00256. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25309317 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effects of the recurrent social isolation stress on fear extinction and dopamine D2 receptors in the amygdala and the hippocampus.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Feb;75(1):119-127. doi: 10.1007/s43440-022-00430-8. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36385611 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Allopregnanolone on Enzymatic Activity of the DNA Base Excision Repair Pathway in the Sheep Hippocampus and Amygdala under Natural and Stressful Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 20;21(20):7762. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207762. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33092287 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Fear Extinction: Pharmacological Approaches.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2023;64:289-305. doi: 10.1007/7854_2023_443. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37584834
-
Exploring Refinement Strategies for Single Housing of Male C57BL/6JRj Mice: Effect of Cage Divider on Stress-Related Behavior and Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal-Axis Activity.Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 Oct 28;15:743959. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.743959. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34776890 Free PMC article.
-
A neurochemical basis for an epigenetic vision of psychiatric disorders (1994-2009).Pharmacol Res. 2011 Oct;64(4):344-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2011.05.026. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Pharmacol Res. 2011. PMID: 21699980 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Valzelli L. Aggressive behavior induced by isolation. In: Garattini S, Sigg SB, editors. Aggressive Behavior. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica Foundation; 1969. pp. 70–76.
-
- Matsumoto K, Puia G, Dong E, Pinna G. GABAA receptor neurotransmission dysfunction in a mouse model of social isolation-induced stress: Possible insights into a non-serotonergic mechanism of action of SSRIs in mood and anxiety disorders. Stress. 2007;10:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto K, et al. Permissive role of brain allopregnanolone content in the regulation of pentobarbital-induced righting reflex loss. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:955–963. - PubMed
-
- Puia G, et al. Neurosteroids act on recombinant human GABAA receptors. Neuron. 1990;4:759–765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

