Structural analysis of the complex of Keap1 with a prothymosin alpha peptide
- PMID: 18391415
- PMCID: PMC2374262
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309108004995
Structural analysis of the complex of Keap1 with a prothymosin alpha peptide
Abstract
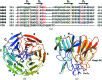
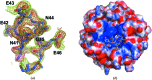
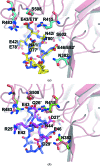
The Nrf2 transcription factor, which plays important roles in oxidative and xenobiotic stress, is negatively regulated by the cytoplasmic repressor Keap1. The beta-propeller/Kelch domain of Keap1, which is formed by the double-glycine repeat and C-terminal region domains (Keap1-DC), interacts directly with the Neh2 domain of Nrf2. The nuclear oncoprotein prothymosin alpha (ProTalpha) also interacts directly with Keap1 and may play a role in the dissociation of the Keap1-Nrf2 complex. The structure of Keap1-DC complexed with a ProTalpha peptide (amino acids 39-54) has been determined at 1.9 A resolution. The Keap1-bound ProTalpha peptide possesses a hairpin conformation and binds to the Keap1 protein at the bottom region of the beta-propeller domain. Complex formation occurs as a consequence of their complementary electrostatic interactions. A comparison of the present structure with recently reported Keap1-DC complex structures revealed that the DLG and ETGE motifs of the Neh2 domain of Nrf2 and the ProTalpha peptide bind to Keap1 in a similar manner but with different binding potencies.
Figures

References
-
- Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4 (1994). Acta Cryst. D50, 760–763. - PubMed
-
- Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. (2004). Acta Cryst. D60, 2126–2132. - PubMed
-
- Evstafieva, A. G., Belov, G. A., Rubtsov, Y. P., Kalkum, M., Joseph, B., Chichkova, N. V., Sukhacheva, E. A., Bogdanov, A. A., Pettersson, R. F., Agol, V. I. & Vartapetian, A. B. (2003). Exp. Cell Res. 284, 211–223. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Marquez, J., Segade, F., Dosil, M., Pichel, J. G., Bustelo, X. R. & Freire, M. (1989). J. Biol. Chem. 264, 8451–8454. - PubMed
-
- Itoh, K., Chiba, T., Takahashi, S., Ishii, T., Igarashi, K., Katoh, Y., Oyake, T., Hayashi, N., Satoh, K., Hatayama, I., Yamamoto, M. & Nabeshima, Y. (1997). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 236, 313–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

