Identification of ten loci associated with height highlights new biological pathways in human growth
- PMID: 18391950
- PMCID: PMC2687076
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.125
Identification of ten loci associated with height highlights new biological pathways in human growth
Abstract
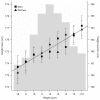
Height is a classic polygenic trait, reflecting the combined influence of multiple as-yet-undiscovered genetic factors. We carried out a meta-analysis of genome-wide association study data of height from 15,821 individuals at 2.2 million SNPs, and followed up the strongest findings in >10,000 subjects. Ten newly identified and two previously reported loci were strongly associated with variation in height (P values from 4 x 10(-7) to 8 x 10(-22)). Together, these 12 loci account for approximately 2% of the population variation in height. Individuals with < or =8 height-increasing alleles and > or =16 height-increasing alleles differ in height by approximately 3.5 cm. The newly identified loci, along with several additional loci with strongly suggestive associations, encompass both strong biological candidates and unexpected genes, and highlight several pathways (let-7 targets, chromatin remodeling proteins and Hedgehog signaling) as important regulators of human stature. These results expand the picture of the biological regulation of human height and of the genetic architecture of this classical complex trait.
Figures
Comment in
-
Sizing up human height variation.Nat Genet. 2008 May;40(5):489-90. doi: 10.1038/ng0508-489. Nat Genet. 2008. PMID: 18443579 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 5 R01 DK 075787/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084729/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL084729/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK62370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 089061/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK72193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002651/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01CA098233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075787/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA49449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P01CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HG02651/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

