Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation
- PMID: 18391953
- PMCID: PMC3766631
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.118
Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation
Abstract
The effects of alleles in many genes are believed to contribute to common complex diseases such as hypertension. Whether risk alleles comprise a small number of common variants or many rare independent mutations at trait loci is largely unknown. We screened members of the Framingham Heart Study (FHS) for variation in three genes-SLC12A3 (NCCT), SLC12A1 (NKCC2) and KCNJ1 (ROMK)-causing rare recessive diseases featuring large reductions in blood pressure. Using comparative genomics, genetics and biochemistry, we identified subjects with mutations proven or inferred to be functional. These mutations, all heterozygous and rare, produce clinically significant blood pressure reduction and protect from development of hypertension. Our findings implicate many rare alleles that alter renal salt handling in blood pressure variation in the general population, and identify alleles with health benefit that are nonetheless under purifying selection. These findings have implications for the genetic architecture of hypertension and other common complex traits.
Figures


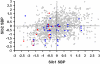
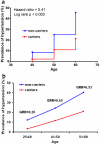
Comment in
-
Salt wasting and blood pressure.Nat Genet. 2008 May;40(5):495-6. doi: 10.1038/ng0508-495. Nat Genet. 2008. PMID: 18443583 No abstract available.
References
-
- Levy D, et al. Evidence for a gene influencing blood pressure on chromosome 17. Genome scan linkage results for longitudinal blood pressure phenotypes in subjects from the framingham heart study. Hypertension. 2000;36:477–83. - PubMed
-
- Saxena R, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science. 2007;316:1331–6. - PubMed
-
- Helgadottir A, et al. A common variant on chromosome 9p21 affects the risk of myocardial infarction. Science. 2007;316:1491–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

