Metaproteomics provides functional insight into activated sludge wastewater treatment
- PMID: 18392150
- PMCID: PMC2289847
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001778
Metaproteomics provides functional insight into activated sludge wastewater treatment
Abstract
Background: Through identification of highly expressed proteins from a mixed culture activated sludge system this study provides functional evidence of microbial transformations important for enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR).
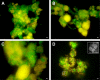
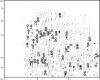
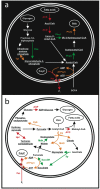
Methodology/principal findings: A laboratory-scale sequencing batch reactor was successfully operated for different levels of EBPR, removing around 25, 40 and 55 mg/l P. The microbial communities were dominated by the uncultured polyphosphate-accumulating organism "Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis". When EBPR failed, the sludge was dominated by tetrad-forming alpha-Proteobacteria. Representative and reproducible 2D gel protein separations were obtained for all sludge samples. 638 protein spots were matched across gels generated from the phosphate removing sludges. 111 of these were excised and 46 proteins were identified using recently available sludge metagenomic sequences. Many of these closely match proteins from "Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis" and could be directly linked to the EBPR process. They included enzymes involved in energy generation, polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis, glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogen synthesis, glyoxylate/TCA cycle, fatty acid beta oxidation, fatty acid synthesis and phosphate transport. Several proteins involved in cellular stress response were detected.
Conclusions/significance: Importantly, this study provides direct evidence linking the metabolic activities of "Accumulibacter" to the chemical transformations observed in EBPR. Finally, the results are discussed in relation to current EBPR metabolic models.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- DeLong EF, Preston CM, Mincer T, Rich V, Hallam SJ, et al. Community genomics among stratified microbial assemblages in the ocean's interior. Science. 2006;311:496–503. - PubMed
-
- Venter JC, Remington K, Heidelberg JF, Halpern AL, Rusch D, et al. Environmental genome shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science. 2004;304:66–74. - PubMed
-
- García-Martín H, Ivanovan N, Kunin V, Warnecke F, Barry KW, et al. Metagenomic analysis of two enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) sludge communities. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:1263–1269. - PubMed
-
- Wilmes P, Bond PL. The application of two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and downstream analyses to a mixed community of prokaryotic microorganisms. Environ Microbiol. 2004;6:911–920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

