Assessment of diesel particulate matter exposure in the workplace: freight terminals
- PMID: 18392272
- PMCID: PMC2386142
- DOI: 10.1039/b715429a
Assessment of diesel particulate matter exposure in the workplace: freight terminals
Abstract
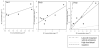
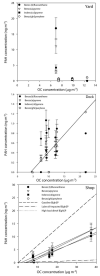
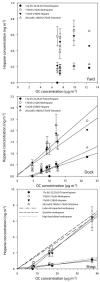
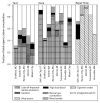
A large study has been undertaken to assess the exposure to diesel exhaust within diesel trucking terminals. A critical component of this assessment is an analysis of the variation in carbonaceous particulate matter (PM) across trucking terminal locations; consistency in the primary sources can be effectively tracked by analyzing trends in elemental carbon (EC) and organic molecular marker concentrations. Ambient samples were collected at yard, dock and repair shop work stations in 7 terminals in the USA and 1 in Mexico. Concentrations of EC ranged from 0.2 to 12 microg m(-3) among the terminals, which corresponds to the range seen in the concentration of summed hopanes (0.5 to 20.5 ng m(-3)). However, when chemical mass balance (CMB) source apportionment results were presented as percent contribution to organic carbon (OC) concentrations, the contribution of mobile sources to OC are similar among the terminals in different cities. The average mobile source percent contribution to OC was 75.3 +/- 17.1% for truck repair shops, 65.4 +/- 20.4% for the docks and 38.4 +/- 9.5% for the terminal yard samples. A relatively consistent mobile source impact was present at all the terminals only when considering percentage of total OC concentrations, not in terms of absolute concentrations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential air toxics hot spots in truck terminals and cabs.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2012 Dec;(172):5-82. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2012. PMID: 23409510 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking personal exposure to particulate diesel exhaust in a diesel freight terminal using organic tracer analysis.J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2009 Feb;19(2):172-86. doi: 10.1038/jes.2008.11. Epub 2008 Mar 5. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2009. PMID: 18322451 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure of trucking company workers to particulate matter during the winter.Chemosphere. 2005 Dec;61(11):1677-90. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.091. Chemosphere. 2005. PMID: 15913707 Free PMC article.
-
Diesel Exhaust Exposure Assessment Among Tunnel Construction Workers-Correlations Between Nitrogen Dioxide, Respirable Elemental Carbon, and Particle Number.Ann Work Expo Health. 2017 Jun 1;61(5):539-553. doi: 10.1093/annweh/wxx024. Ann Work Expo Health. 2017. PMID: 28371844
-
Particulate matter in new technology diesel exhaust (NTDE) is quantitatively and qualitatively very different from that found in traditional diesel exhaust (TDE).J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2011 Sep;61(9):894-913. doi: 10.1080/10473289.2011.599277. J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2011. PMID: 22010375 Review.
Cited by
-
Lung cancer and vehicle exhaust in trucking industry workers.Environ Health Perspect. 2008 Oct;116(10):1327-32. doi: 10.1289/ehp.11293. Epub 2008 May 30. Environ Health Perspect. 2008. PMID: 18941573 Free PMC article.
-
Lung cancer and elemental carbon exposure in trucking industry workers.Environ Health Perspect. 2012 Sep;120(9):1301-6. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1204989. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Environ Health Perspect. 2012. PMID: 22739103 Free PMC article.
-
Ischaemic heart disease mortality and years of work in trucking industry workers.Occup Environ Med. 2013 Aug;70(8):523-8. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2011-100017. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Occup Environ Med. 2013. PMID: 22992341 Free PMC article.
-
Underground Gold Miner Exposure to Noise, Diesel Particulate Matter and Crystalline Silica Dust.J Health Pollut. 2021 Feb 25;11(29):210301. doi: 10.5696/2156-9614-11.29.210301. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Health Pollut. 2021. PMID: 33815899 Free PMC article.
-
Occupational Respirable Mine Dust and Diesel Particulate Matter Hazard Assessment in an Underground Gold Mine in Ghana.J Health Pollut. 2020 Feb 28;10(25):200305. doi: 10.5696/2156-9614-10.25.200305. eCollection 2020 Mar. J Health Pollut. 2020. PMID: 32175176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garshick E, Schenker MB, Munoz A, Segal M, Smith TJ, Woskie SR, Hammond SK, Speizer FE. A Case-Control Study Of Lung-Cancer And Diesel Exhaust Exposure In Railroad Workers. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987;135(6):1242–1248. - PubMed
-
- Garshick E, Schenker MB, Munoz A, Segal M, Smith TJ, Woskie SR, Hammond SK, Speizer FE. A Retrospective Cohort Study Of Lung-Cancer And Diesel Exhaust Exposure In Railroad Workers. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1988;137(4):820–825. - PubMed
-
- Laden F, Hart JE, Eisen E, Davis M, Smith TJ, Speizer FE, Garshick E. Lung cancer mortality in a retrospective cohort of drivers in the US trucking industry. Epidemiology. 2006;17(6):S173–S174.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

