Immunomodulatory drugs Revlimid (lenalidomide) and CC-4047 induce apoptosis of both hematological and solid tumor cells through NK cell activation
- PMID: 18392823
- PMCID: PMC11030653
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-008-0512-7
Immunomodulatory drugs Revlimid (lenalidomide) and CC-4047 induce apoptosis of both hematological and solid tumor cells through NK cell activation
Abstract
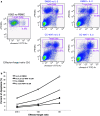
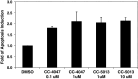
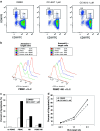
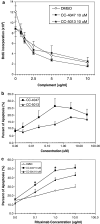
Revlimid (Lenalidomide, CC-5013) and CC-4047 are IMiDs immunomodulatory drugs that have been described as having immunomodulatory properties and anti-tumor activity. Here we report proapoptotic effects of CC-5013 and CC-4047 on tumor cells in a co-culture model of PBMC and tumor cells. CC-5013 and CC-4047 enhanced PBMC activity leading to tumor cell apoptosis in K562/PBMC co-culture model. We also demonstrate that the natural killer (NK) cell population of PBMC was essential in inducing K562 apoptosis. Increases of NK and natural killer T (NKT) cell populations by CC-5013 and CC-4047 was observed along with modulation of NK cell CD56 adhesion marker. In addition, our data indicate that NK activation by CC-4047 was dependent on other cell types of PBMC. We expanded the application of K562/PBMC co-culture model to other hematological and solid tumors. In Raji/PBMC co-culture model, CC-5013 and CC-4047 dose-dependently augmented tumor cell apoptosis. Pre-treatment of Raji cells with Rituximab further enhanced apoptosis induced by CC-5013 or CC-4047-treated PBMC. Moreover, CC-5013 and CC-4047 significantly increased PC-3 prostate cancer cell apoptosis in PC-3/PBMC co-culture, either as single agent or in combination with Docetaxel. Together, the results reveal that co-culture models are suitable cellular systems to assess anti-tumor activities of these compounds. Our findings support clinical evaluation of CC-5013 and CC-4047 in relapsed NHL with Rituximab and in prostate cancer with Docetaxel.
Figures
References
-
- Bartlett JB, Michael A, Clarke IA, Dredge K, Nicholson S, Kristeleit H, Polychronis A, Pandha H, Muller GW, Stirling DI, Zeldis J, Dalgleish AG. Phase I study to determine the safety, tolerability and immunostimulatory activity of thalidomide analogue CC-5013 in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma and other advanced cancers. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:955–961. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601579. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartlett JB, Wu L, Adams M, Schafer P, Muller G, Stirling D (2007) lenalidomide and pomalidomide strongly enhance tumor cell killing in vitro during antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) mediated by trastuzumab, cetuximab and rituximab. Paper presented at 2007 ASCO annual meeting abstract 3023
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

