Apolipoprotein B-dependent hepatitis C virus secretion is inhibited by the grapefruit flavonoid naringenin
- PMID: 18393287
- PMCID: PMC4500072
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.22197
Apolipoprotein B-dependent hepatitis C virus secretion is inhibited by the grapefruit flavonoid naringenin
Abstract
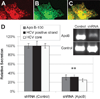
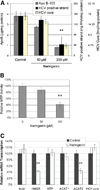
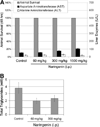
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infects over 3% of the world population and is the leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. HCV has long been known to associate with circulating lipoproteins, and its interactions with the cholesterol and lipid pathways have been recently described. In this work, we demonstrate that HCV is actively secreted by infected cells through a Golgi-dependent mechanism while bound to very low density lipoprotein (vLDL). Silencing apolipoprotein B (ApoB) messenger RNA in infected cells causes a 70% reduction in the secretion of both ApoB-100 and HCV. More importantly, we demonstrate that the grapefruit flavonoid naringenin, previously shown to inhibit vLDL secretion both in vivo and in vitro, inhibits the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein activity as well as the transcription of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase 2 in infected cells. Stimulation with naringenin reduces HCV secretion in infected cells by 80%. Moreover, we find that naringenin is effective at concentrations that are an order of magnitude below the toxic threshold in primary human hepatocytes and in mice.
Conclusion: These results suggest a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of HCV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report.
Figures


Comment in
-
A grapefruit a day for patients infected with hepatitis C?Hepatology. 2008 Jun;47(6):2141-2; author reply 2142-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.22308. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18508304 No abstract available.
References
-
- Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis. 2006;1:23–61. - PubMed
-
- Thomssen R, Bonk S, Propfe C, Heermann KH, Kochel HG, Uy A. Association of hepatitis C virus in human sera with beta-lipoprotein. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181:293–300. - PubMed
-
- Monazahian M, Kippenberger S, Muller A, Seitz H, Bohme I, Grethe S, et al. Binding of human lipoproteins (low, very low, high density lipoproteins) to recombinant envelope proteins of hepatitis C virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2000;188:177–184. - PubMed
-
- Sabile A, Perlemuter G, Bono F, Kohara K, Demaugre F, Kohara M, et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein binds to apolipoprotein AII and its secretion is modulated by fibrates. Hepatology. 1999;30:1064–1076. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
