Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by NF-kappaB
- PMID: 18393939
- PMCID: PMC2474706
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20080476
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by NF-kappaB
Abstract
HIF (hypoxia-inducible factor) is the main transcription factor activated by low oxygen tensions. HIF-1alpha (and other alpha subunits) is tightly controlled mostly at the protein level, through the concerted action of a class of enzymes called PHDs (prolyl hydroxylases) 1, 2 and 3. Most of the knowledge of HIF derives from studies following hypoxic stress; however, HIF-1alpha stabilization is also found in non-hypoxic conditions through an unknown mechanism. In the present study, we demonstrate that NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappaB) is a direct modulator of HIF-1alpha expression. The HIF-1alpha promoter is responsive to selective NF-kappaB subunits. siRNA (small interfering RNA) studies for individual NF-kappaB members revealed differential effects on HIF-1alpha mRNA levels, indicating that NF-kappaB can regulate basal HIF-1alpha expression. Finally, when endogenous NF-kappaB is induced by TNFalpha (tumour necrosis factor alpha) treatment, HIF-1alpha levels also change in an NF-kappaB-dependent manner. In conclusion, we find that NF-kappaB can regulate basal TNFalpha and, in certain circumstances, the hypoxia-induced HIF-1alpha.
Figures

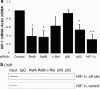
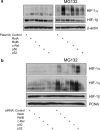
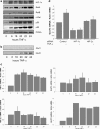

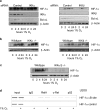
Comment in
-
The cross-talk between NF-kappaB and HIF-1: further evidence for a significant liaison.Biochem J. 2008 Jun 15;412(3):e17-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080920. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18498249
References
-
- Bardos J. I., Ashcroft M. Negative and positive regulation of HIF-1: a complex network. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2005;1755:107–120. - PubMed
-
- Garcia J. A. HIFing the brakes: therapeutic opportunities for treatment of human malignancies. Science STKE. 2006 PE25. - PubMed
-
- Dery M. A., Michaud M. D., Richard D. E. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: regulation by hypoxic and non-hypoxic activators. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005;37:535–540. - PubMed
-
- Fandrey J., Gorr T. A., Gassmann M. Regulating cellular oxygen sensing by hydroxylation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006;71:642–651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

