Reassortant avian influenza virus (H5N1) in poultry, Nigeria, 2007
- PMID: 18394282
- PMCID: PMC2570913
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1404.071178
Reassortant avian influenza virus (H5N1) in poultry, Nigeria, 2007
Erratum in
- Emerg Infect Dis. 2008 May;14(5):865
Abstract
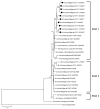
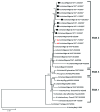
Genetic characterization of a selection of influenza virus (H5N1) samples, circulating in 8 Nigerian states over a 39-day period in early 2007, indicates that a new reassortant strain is present in 7 of the 8 states. Our study reports an entirely different influenza virus (H5N1) reassortant becoming predominant and widespread in poultry.
Figures
References
-
- European Commission. Council Directive 2005 94/ECC. Community measures for the control of avian influenza and repealing directive 92/40/EEC. Official Journal of the European Union. 2005;L010 [cited 2005 Dec 20]. Available from http://eur-lex.europa.eu/en/dossier/dossier_04.htm
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
