PWZ-029, a compound with moderate inverse agonist functional selectivity at GABA(A) receptors containing alpha5 subunits, improves passive, but not active, avoidance learning in rats
- PMID: 18394590
- PMCID: PMC2577822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.020
PWZ-029, a compound with moderate inverse agonist functional selectivity at GABA(A) receptors containing alpha5 subunits, improves passive, but not active, avoidance learning in rats
Abstract
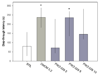
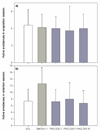
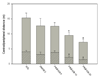
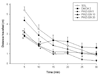
Benzodiazepine (BZ) site ligands affect vigilance, anxiety, memory processes, muscle tone and epileptogenic propensity through modulation of neurotransmission at GABA(A) receptors containing alpha1, alpha2, alpha3 or alpha5 subunits, and may have numerous experimental and clinical applications. The ability of non-selective BZ site inverse agonists to enhance cognition, documented in animal models and human studies, is clinically not feasible due to potentially unacceptable psychomotor effects. Most investigations to date have proposed the alpha1 and/or alpha5 subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors as comprising the memory-modulating population of these receptors. The novel ligand PWZ-029, which we synthesized and characterized electrophysiologically, possesses in vitro binding selectivity and moderate inverse agonist functional selectivity at alpha5-containing GABA(A) receptors. This ligand has also been examined in rats in the passive and active avoidance, spontaneous locomotor activity, elevated plus maze and grip strength tests, primarily predictive of the effects on the memory acquisition, basal locomotor activity, anxiety level and muscle tone, respectively. The improvement of task learning was detected at the dose of 5 mg/kg in the passive, but not active avoidance test. The inverse agonist PWZ-029 had no effect on anxiety or muscle tone, whereas at higher doses (10 and 20 mg/kg) it decreased locomotor activity. This effect was antagonized by flumazenil and also by the lower (but not the higher) dose of an agonist (SH-053-R-CH3-2'F) selective for GABA(A) receptors containing the alpha5 subunit. The hypolocomotor effect of PWZ-029 was not antagonized by the antagonist ss-CCt exhibiting a preferential affinity for alpha1-subunit-containing receptors. These data suggest that moderate negative modulation at GABA(A) receptors containing the alpha5 subunit is a sufficient condition for eliciting enhanced encoding/consolidation of declarative memory, while the influence of higher doses of modulators at these receptors on motor activity shows an intricate pattern whose relevance and mechanism await to be defined.
Figures



References
-
- Atack JR, Bayley PJ, Seabrook GR, Wafford KA, McKernan RM, Dawson GR. L-655,708 enhances cognition in rats but is not proconvulsant at a dose selective for alpha5-containing GABAA receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2006a;51:1023–1029. - PubMed
-
- Atack JR, Wafford KA, Tye SJ, Cook SM, Sohal B, Pike A, Sur C, Melillo D, Bristow L, Bromidge F, Ragan I, Kerby J, Street L, Carling R, Castro JL, Whiting P, Dawson GR, McKernan RM. TPA023 [7-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-6-(2-ethyl-2H-1,2,4-triazol-3-ylmethoxy)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine], an agonist selective for alpha2- and alpha3-containing GABAA receptors, is a nonsedating anxiolytic in rodents and primates. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006b;316:410–422. - PubMed
-
- Benson JA, Low K, Keist R, Möhler H, Rudolph U. Pharmacology of recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors rendered diazepam-insensitive by point-mutated alpha-subunits. FEBS Lett. 1998;431:400–404. - PubMed
-
- Chambers MS, Atack JR, Broughton HB, Collinson N, Cook S, Dawson GR, Hobbs SC, Marshall G, Maubach KA, Pillai GV, Reeve AJ, MacLeod AM. Identification of a novel, selective GABA(A) alpha5 receptor inverse agonist which enhances cognition. J. Med. Chem. 2003;46:2227–2240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

