Gliadin activates HLA class I-restricted CD8+ T cells in celiac disease intestinal mucosa and induces the enterocyte apoptosis
- PMID: 18395083
- PMCID: PMC3319059
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.01.008
Gliadin activates HLA class I-restricted CD8+ T cells in celiac disease intestinal mucosa and induces the enterocyte apoptosis
Abstract
Background & aims: The extensive infiltration of CD8(+) T cells in the intestinal mucosa of celiac disease (CD) patients is a hallmark of the disease. We identified a gliadin peptide (pA2) that is selectively recognized by CD8(+) T cells infiltrating intestinal mucosa of HLA-A2(+) CD patients. Herein, we investigated the phenotype, the tissue localization, and the effector mechanism of cells responsive to pA2 by using the organ culture of CD intestinal mucosa. The target of pA2-mediated cytotoxicity was also investigated by using the intestinal epithelial cell lines Caco2 and HT29, A2(+) and A2(-), respectively, as target cells.
Methods: Jejunal biopsy specimens from CD patients were cultured in vitro with pA2, and cellular activation was evaluated by immunohistochemistry and cytofluorimetric analysis. Cytotoxicity of pA2-specific, intestinal CD8(+) T cells was assayed by granzyme-B and interferon-gamma release and by apoptosis of target cells.
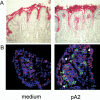
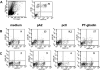
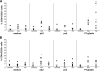
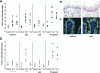
Results: pA2 challenge of A2(+) CD mucosa increased the percentage of CD8(+)CD25(+) and of CD80(+) cells in the lamina propria, the former mainly localized beneath the epithelium, as well as the number of terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling-positive cells (TUNEL(+)) in the epithelium. Intraepithelial CD3(+) cells and enterocyte expression of Fas were also increased. CD8(+)CD25(+) and CD8(+)FASL(+) T cells were significantly increased in cell preparations from biopsy specimens cultured with pA2. CD8(+) T-cell lines released both granzyme-B and interferon-gamma following recognition of pA2 when presented by Caco2 and not by HT29.
Conclusions: These data indicate that gliadins contain peptides able to activate, through a TCR/HLA class I interaction, CD8-mediated response in intestinal CD mucosa and to induce the enterocyte apoptosis.
Figures



References
-
- Sollid LM. Celiac disease: dissecting a complex inflammatory disorder. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:647–655. - PubMed
-
- Troncone R, Gianfrani C, Mazzarella G, et al. Majority of gliadin-specific T-cell clones from celiac small intestinal mucosa produce interferon-γ and interleukin-4. Dig Dis Sci. 1998;43:156–161. - PubMed
-
- Gianfrani C, Troncone R, Magione P, et al. Celiac disease association with CD8+ T-cell responses: identification of a novel gliadin-derived HLA-A2 restricted epitope. J Immunol. 2003;170:2719–2726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

