Lymphoid neogenesis and immune infiltration in aged liver
- PMID: 18395842
- PMCID: PMC2859446
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.22224
Lymphoid neogenesis and immune infiltration in aged liver
Abstract
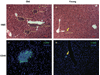
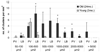
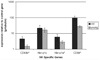
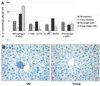
Immune dysregulation and inflammation play a major role in the pathology of age-related disorders. In an earlier study, the microarray data from our laboratory indicated an increase in inflammation-related gene expression in the liver with age. We further investigated immune-related changes in the aged liver and found that the levels of inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and inflammatory genes were higher in aged animals. Immunohistochemical studies showed that immune cells formed clusters or foci in the livers of old mice, preferentially near the perivascular regions. Further analysis revealed an enrichment of macrophages, T cells, B cells, natural killer cells, and neutrophils in old liver. Characterization of the immune clusters showed the presence of shared markers of tertiary lymphoid neogenesis. Levels of lymph node homing cytokines were elevated. Expression of immunoglobulin and recombinase gene transcripts was also higher, indicating the presence of ectopic lymphoid structures in the aged liver.
Conclusion: Aged liver exhibits a marked inflammatory status accompanied by increased immune cell infiltration. Inflammation and ectopic lymphoid structures have previously been shown to be associated with carcinogenesis, a condition that becomes more prevalent with age. Thus, further study of inflammation-related changes in the microenvironment of the aged liver could provide insights into these disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inflammation and ectopic lymphoid structures in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues dissected by genomics technology: identification of the interleukin-7 signaling pathway in tissues with lymphoid neogenesis.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Aug;56(8):2492-502. doi: 10.1002/art.22748. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17665400
-
Elevated interferon gamma signaling contributes to impaired regeneration in the aged liver.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011 Sep;66(9):944-56. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glr094. Epub 2011 Jun 30. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21719609 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of ectopic lymphoid neogenesis and in situ autoantibody production in autoimmune nonobese diabetic mice: cellular and molecular characterization of tertiary lymphoid structures in pancreatic islets.J Immunol. 2010 Sep 15;185(6):3359-68. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001836. Epub 2010 Aug 16. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20713891
-
Ectopic lymphoid follicles: inducible centres for generating antigen-specific immune responses within tissues.Immunology. 2016 Feb;147(2):141-51. doi: 10.1111/imm.12554. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Immunology. 2016. PMID: 26551738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular analysis of mouse T cell receptor expression using PCR.Curr Protoc Immunol. 2001 May;Chapter 10:10.27.1-10.27.20. doi: 10.1002/0471142735.im1027s22. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2001. PMID: 18432692 Review.
Cited by
-
Ectopic lymphoid structures in the aged lacrimal glands.Clin Immunol. 2023 Mar;248:109251. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109251. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36740002 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of recipient age on the effects of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure and liver cirrhosis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Aug 20;12(1):466. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02544-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34416908 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of low and high plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) on the morphology of major organs: studies of Laron dwarf and bovine growth hormone transgenic (bGHTg) mice.Histol Histopathol. 2013 Oct;28(10):1325-36. doi: 10.14670/HH-28.1325. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Histol Histopathol. 2013. PMID: 23613169 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-profiles of gene expression during aging: limited similarities between mouse and human and an unexpectedly decreased inflammatory signature.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33204. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033204. Epub 2012 Mar 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22413003 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of apoptosis on liver aging.World J Clin Cases. 2019 Mar 26;7(6):691-704. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i6.691. World J Clin Cases. 2019. PMID: 30968034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Franceschi C, Bonafè M, Valensin S, Olivieri F, De Luca M, Ottaviani E, et al. Inflammaging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;908:244–254. - PubMed
-
- Golden TR, Melov S. Microarray analysis of gene expression with age in individual nematodes. Aging Cell. 2004;3:111–124. - PubMed
-
- Couillault C, Pujol N, Reboul J, Sabatier L, Guichou JF, Kohara Y, et al. TLR-independent control of innate immunity in Caenorhabditis elegans by the TIR domain adaptor protein TIR-1, an ortholog of human SARM. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:488–494. - PubMed
-
- Baggio G, Donazzan S, Monti D, Mari D, Martini S, Gabelli C, et al. Lipoprotein(a) and lipoprotein profile in healthy centenarians: a reappraisal of vascular risk factors. FASEB J. 1998;12:433–437. - PubMed
-
- Ershler WB, Sun WH, Binkley N, Gravenstein S, Volk MJ, Kamoske G, et al. Interleukin-6 and aging: blood levels and mononuclear cell production increase with advancing age and in vitro production is modifiable by dietary restriction. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1993;12:225–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
