Serum type IV collagen level is predictive for esophageal varices in patients with severe alcoholic disease
- PMID: 18395904
- PMCID: PMC2701525
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.2044
Serum type IV collagen level is predictive for esophageal varices in patients with severe alcoholic disease
Abstract
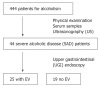
Aim: To determine factors predictive for esophageal varices in severe alcoholic disease (SAD).
Methods: Abdominal ultrasonography (US) was performed on 444 patients suffering from alcoholism. Forty-four patients found to have splenomegaly and/ or withering of the right liver lobe were defined as those with SAD. SAD patients were examined by upper gastrointestinal (UGI) endoscopy for the presence of esophageal varices. The existence of esophageal varices was then related to clinical variables.
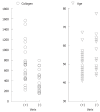
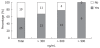
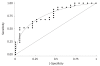
Results: Twenty-five patients (56.8%) had esophageal varices. A univariate analysis revealed a significant difference in age and type IV collagen levels between patients with and without esophageal varices. A logistic regression analysis identified type IV collagen as the only independent variable predictive for esophageal varices (P = 0.017). The area under the curve (AUC) for type IV collagen as determined by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) for predicting esophageal varices was 0.78.
Conclusion: This study suggests that the level of type IV collagen has a high diagnostic accuracy for the detection of esophageal varices in SAD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Albumin and magnetic resonance imaging-liver volume to identify hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and esophageal varices.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 21;21(3):988-96. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.988. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25624735 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet count to splenic diameter ratio and other noninvasive markers as predictors of esophageal varices in patients with liver cirrhosis.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017 Sep;28(5):347-352. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2017.17090. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28776495
-
Prediction of large esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis of the liver using clinical, laboratory and imaging parameters.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Nov;22(11):1909-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04501.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17914969
-
A Beginning or the End? A Meta-analysis to Assess the Diagnostic Accuracy of Transient Elastography for the Prediction of Esophageal Varices.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2016 Sep-Oct;22(5):345-352. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.191138. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27748319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening for esophageal varices.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2012 Nov 9;1(5):143-146. doi: 10.1002/cld.101. eCollection 2012 Nov. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 31186874 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Towards noninvasive detection of oesophageal varices.Int J Hepatol. 2012;2012:343591. doi: 10.1155/2012/343591. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Int J Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22506126 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive assessment of portal hypertension in cirrhosis: liver stiffness and beyond.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 7;20(45):16811-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.16811. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25492995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sonographic gallbladder wall thickness measurement and the prediction of esophageal varices among cirrhotics.World J Hepatol. 2023 Feb 27;15(2):216-224. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i2.216. World J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36926231 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sutton R, Shields R. Alcohol and oesophageal varices. Alcohol Alcohol. 1995;30:581–589. - PubMed
-
- Merli M, Nicolini G, Angeloni S, Rinaldi V, De Santis A, Merkel C, Attili AF, Riggio O. Incidence and natural history of small esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients. J Hepatol. 2003;38:266–272. - PubMed
-
- D'Amico G, Morabito A. Noninvasive markers of esophageal varices: another round, not the last. Hepatology. 2004;39:30–34. - PubMed
-
- Groszmann RJ, de Franchis R, In: Schiff ER, Sorrell MF, Maddrey WC Portal hypertension. Philadelphia, New York: Lippincott-Raven; 1999. Schiff’s Disease of the Liver; pp. 387–442.
-
- Sharara AI, Rockey DC. Gastroesophageal variceal hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:669–681. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

