Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis by KLF4
- PMID: 18396140
- PMCID: PMC2430156
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.02.001
Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis by KLF4
Abstract
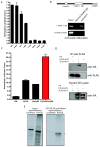
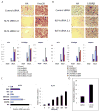
While adipogenesis is known to be controlled by a complex network of transcription factors, less is known about the transcriptional cascade that initiates this process. We report here the characterization of Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) as an essential early regulator of adipogenesis. Klf4 is expressed in 3T3-L1 cells within 30 min after exposure to a standard adipogenic cocktail of insulin, glucocorticoids, and IBMX. Knockdown of KLF4 inhibits adipogenesis and downregulates C/EBPbeta levels. KLF4 binds directly to the C/EBPbeta (Cebpb) promoter as shown by chromatin immunoprecipitation and gel shift assays and, together with Krox20, cooperatively transactivates a C/EBPbeta reporter. C/EBPbeta knockdown increases levels of KLF4 and Krox20, suggesting that C/EBPbeta normally suppresses Krox20 and KLF4 expression via a tightly controlled negative feedback loop. KLF4 is specifically induced in response to cAMP, which by itself can partially activate adipogenesis. These data suggest that KLF4 functions as an immediate early regulator of adipogenesis to induce C/EBPbeta.
Figures


References
-
- Boyer-Guittaut M, Birsoy K, Potel C, Elliot G, Jaffray E, Desterro J, Hay R, Oelgeschläger T. SUMO-1 modification of human transcription factor (TF) IID complex subunits. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:9937–9945. - PubMed
-
- Cao Z, Umek RM, McKnight SL. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991;5:1538–1552. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Torrens JI, Anand A, Spiegelman BM, Friedman J. Krox20 stimulates adipogenesis via C/EBP b-dependent and - independent mechanisms. Cell Metabolism. 2005;1:93–106. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

