Technological development and advances in single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography
- PMID: 18396178
- PMCID: PMC3049175
- DOI: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2008.01.001
Technological development and advances in single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography
Abstract
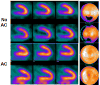
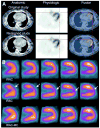
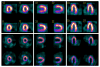
Single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT) has emerged during the past decade as a means of correlating anatomical information from CT with functional information from SPECT. The integration of SPECT and CT in a single imaging device facilitates anatomical localization of the radiopharmaceutical to differentiate physiological uptake from that associated with disease and patient-specific attenuation correction to improve the visual quality and quantitative accuracy of the SPECT image. The first clinically available SPECT/CT systems performed emission-transmission imaging using a dual-headed SPECT camera and a low-power x-ray CT subsystem. Newer SPECT/CT systems are available with high-power CT subsystems suitable for detailed anatomical diagnosis, including CT coronary angiography and coronary calcification that can be correlated with myocardial perfusion measurements. The high-performance CT capabilities also offer the potential to improve compensation of partial volume errors for more accurate quantitation of radionuclide measurement of myocardial blood flow and other physiological processes and for radiation dosimetry for radionuclide therapy. In addition, new SPECT technologies are being developed that significantly improve the detection efficiency and spatial resolution for radionuclide imaging of small organs including the heart, brain, and breast, and therefore may provide new capabilities for SPECT/CT imaging in these important clinical applications.
Figures









References
-
- Cherry SR, Sorenson JA, Phelps ME. Physics in Nuclear Medicine. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2003.
-
- Jaszczak RJ, Coleman RE, Lim CB. SPECT: Single photon emission computed tomography. IEEE Tran Nucl Sci. 1980;NS-27:1137–1153.
-
- Loats H. CT and SPECT image registration and fusion for spatial localization of metastatic processes using radiolabeled monoclonals. J Nucl Med. 1993;34:562–566. - PubMed
-
- Maintz JB, Viergever MA. A survey of medical image registration. Med Image Anal. 1998;2:1–36. - PubMed
-
- Hill DL, Batchelor PG, Holden M, Hawkes DJ. Medical image registration. Phys Med Biol. 2001;46:R1–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 4 R44 EB001685/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 2 R44 ES012361/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000288/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 2 R44 H083494/PHS HHS/United States
- K25 CA114254/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB001685/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R44 ES012361/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R41 AG030241/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R21 HL083073/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R44 CA095936/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL083073/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB006373/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 2 R44 CA095936/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R41 AG030241/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5 K25 CA114254/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5 R21 EB006373/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 5 R01 EB000288/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R33 EB001685/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

