Pulse-rate discrimination by cochlear-implant and normal-hearing listeners with and without binaural cues
- PMID: 18397032
- PMCID: PMC2376257
- DOI: 10.1121/1.2874796
Pulse-rate discrimination by cochlear-implant and normal-hearing listeners with and without binaural cues
Abstract
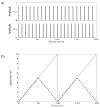
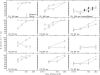
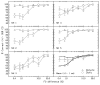
Experiment 1 measured rate discrimination of electric pulse trains by bilateral cochlear implant (CI) users, for standard rates of 100, 200, and 300 pps. In the diotic condition the pulses were presented simultaneously to the two ears. Consistent with previous results with unilateral stimulation, performance deteriorated at higher standard rates. In the signal interval of each trial in the dichotic condition, the standard rate was presented to the left ear and the (higher) signal rate was presented to the right ear; the non-signal intervals were the same as in the diotic condition. Performance in the dichotic condition was better for some listeners than in the diotic condition for standard rates of 100 and 200 pps, but not at 300 pps. It is concluded that the deterioration in rate discrimination observed for CI users at high rates cannot be alleviated by the introduction of a binaural cue, and is unlikely to be limited solely by central pitch processes. Experiment 2 performed an analogous experiment in which 300-pps acoustic pulse trains were bandpass filtered (3900-5400 Hz) and presented in a noise background to normal-hearing listeners. Unlike the results of experiment 1, performance was superior in the dichotic than in the diotic condition.
Figures
References
-
- Baumann U, Nobbe A. Pitch ranking with deeply inserted electrode arrays. Ear and Hearing. 2004;25:275–283. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein LR, Trahiotis C. Detection of interaural delay in high-frequency sinusoidally amplitude-modulated tones, two-tone complexes, and bands of noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994;95:3561–3567. - PubMed
-
- Carlyon RP, Deeks JM. Limitations on rate discrimination. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002;112:1009–1025. - PubMed
-
- Carlyon RP, Mahendran S, Deeks JM, Bleeck S, Winter IM, Axon P, Baguley D. Behavioral and physiological correlates of temporal pitch perception in electric and acoustic hearing; Association for Research in Otolaryngology, 30th Annual Midwinter Research Meeting; Denver, Colorado. 2007. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

