Regulation of the fructose transporter GLUT5 in health and disease
- PMID: 18398011
- PMCID: PMC2652499
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.90245.2008
Regulation of the fructose transporter GLUT5 in health and disease
Abstract
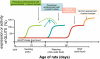
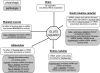
Fructose is now such an important component of human diets that increasing attention is being focused on the fructose transporter GLUT5. In this review, we describe the regulation of GLUT5 not only in the intestine and testis, where it was first discovered, but also in the kidney, skeletal muscle, fat tissue, and brain where increasing numbers of cell types have been found to have GLUT5. GLUT5 expression levels and fructose uptake rates are also significantly affected by diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and inflammation and seem to be induced during carcinogenesis, particularly in the mammary glands. We end by highlighting research areas that should yield information needed to better understand the role of GLUT5 during normal development, metabolic disturbances, and cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham S, Borrebaek B, Chaikoff IL. Effect of dietary carbohydrate and glucokinase and mannokinase activities of various rat tissues. J Nutr 83: 273–288, 1964. - PubMed
-
- Agbemafle BM, Oesterreicher TJ, Shaw CA, Henning SJ. Immediate early genes of glucocorticoid action on the developing intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288: G897–G906, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Angulo C, Rauch MC, Droppelmann A, Reyes AM, Slebe JC, Delgado-Lopez F, Guaiquil VH, Vera JC, Concha II. Hexose transporter expression and function in mammalian spermatozoa: cellular localization and transport of hexoses and vitamin C. J Cell Biochem 71: 189–203, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Asada T, Ogawa T, Iwai M, Shimomura K, Kobayashi M. Recombinant insulin-like growth factor I normalizes expression of renal glucose transporters in diabetic rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 273: F27–F37, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Baba R, Yamami M, Sakuma Y, Fujita M, Fujimoto S. Relationship between glucose transporter and changes in the absorptive system in small intestinal absorptive cells during the weaning process. Med Mol Morphol 38: 47–53, 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

