Epigenetic gene silencing in the Wnt pathway in breast cancer
- PMID: 18398311
- PMCID: PMC7233793
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.3.2.5899
Epigenetic gene silencing in the Wnt pathway in breast cancer
Abstract
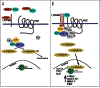
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies in women. Despite advances in treatment of endocrine-dependent tumors, the complete molecular basis of transformation is still unknown. What is clear is that a variety of genetic lesions and epigenetic modifications are present in the neoplasm. Disregulation of several signaling pathways is known to be associated with breast cancer development, among them is the wingless and integration site growth factor (Wnt) pathway. While genetic mutations of certain components of this pathway, such as APC, are significant contributing factors for colorectal cancers, they are typically not the predominate mechanism associated with breast cancer. Instead, it appears that DNA hypermethylation leads to aberrant regulation of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer, and as such, this review focuses on the epigenetic regulation of Wnt pathway components in breast cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Widschwendter M and Jones PA. DNA methylation and breast carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2002; 21:5462–82. - PubMed
-
- Lu Q, Qiu X, Hu N, Wen H, Su Y and Richardson B. Epigenetics, disease, and therapeutic interventions. Ageing Research Reviews 2006; 5:449–67. - PubMed
-
- Agoston AT, Argani P, Yegnasubramanian S, De Marzo AM, Ansari Lari MA, Hicks JL, Davidson NE and Nelson WG. Increased protein stability causes DNA methyltransferase 1 dysregulation in breast cancer. J Biol Chem 2005; 280:18302–10. - PubMed
-
- Girault I, Tozlu S, Lidereau R and Bieche I. Expression analysis of DNA methyltransferases 1, 3A, and 3B in sporadic breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9:4415–22. - PubMed
-
- Jaiswal AS, Balusu R and Narayan S. Involvement of adenomatous polyposis coli in colorectal tumorigenesis. Front Biosci 2005; 10:1118–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
