WAMIDEX: a web atlas of murine genomic imprinting and differential expression
- PMID: 18398312
- PMCID: PMC2492384
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.3.2.5900
WAMIDEX: a web atlas of murine genomic imprinting and differential expression
Abstract
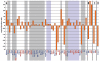
The mouse is an established model organism for the study of genomic imprinting. Mice with genetic material originating from only one parent (e.g., mice with uniparental chromosomal duplications) or gene mutations leading to epigenetic deficiencies have proven to be particularly useful tools. In the process of our studies we have accumulated a large set of expression microarray measurements in samples derived from these types of mice. Here, we present the collation of these and third-party microarray data that are relevant to genomic imprinting into a Web Atlas of Murine genomic Imprinting and Differential EXpression (WAMIDEX: https://atlas.genetics.kcl.ac.uk). WAMIDEX integrates the most comprehensive literature-derived catalog of murine imprinted genes to date with a genome browser that makes the microarray data immediately accessible in annotation-rich genomic context. In addition, WAMIDEX exemplifies the use of the self-organizing map method for the discovery of novel imprinted genes from microarray data. The parent-of-origin-specific expression of imprinted genes is frequently limited to specific tissues or developmental stages, a fact that the atlas reflects in its design and data content.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chromosome-wide identification of novel imprinted genes using microarrays and uniparental disomies.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 19;34(12):e88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl461. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16855283 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic conflict reflected in tissue-specific maps of genomic imprinting in human and mouse.Nat Genet. 2015 May;47(5):544-9. doi: 10.1038/ng.3274. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Nat Genet. 2015. PMID: 25848752 Free PMC article.
-
An oligonucleotide microarray for mouse imprinted genes profiling.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006;113(1-4):253-61. doi: 10.1159/000090840. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 16575188
-
Genome-wide survey of imprinted genes.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006;113(1-4):144-52. doi: 10.1159/000090826. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 16575174 Review.
-
Phenotypic outcomes of imprinted gene models in mice: elucidation of pre- and postnatal functions of imprinted genes.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2014;15:93-126. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153441. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24898037 Review.
Cited by
-
Protection of CpG islands against de novo DNA methylation during oogenesis is associated with the recognition site of E2f1 and E2f2.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2014 Oct 21;7:26. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-7-26. eCollection 2014. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2014. PMID: 25478011 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution analysis of parent-of-origin allelic expression in the mouse brain.Science. 2010 Aug 6;329(5992):643-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1190830. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Science. 2010. PMID: 20616232 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic imprinting in mouse blastocysts is predominantly associated with H3K27me3.Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 21;12(1):3804. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23510-4. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34155196 Free PMC article.
-
The imprinted Zdbf2 gene finely tunes control of feeding and growth in neonates.Elife. 2022 Jan 20;11:e65641. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65641. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35049495 Free PMC article.
-
A survey of tissue-specific genomic imprinting in mammals.Mol Genet Genomics. 2012 Aug;287(8):621-30. doi: 10.1007/s00438-012-0708-6. Epub 2012 Jul 21. Mol Genet Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22821278 Review.
References
-
- da Rocha ST, Ferguson Smith AC. Genomic imprinting. Curr Biol. 2004;14:646–9. - PubMed
-
- Bourc'his D, Proudhon C. Sexual dimorphism in parental imprint ontogeny and contribution to embryonic development. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008;282:87–94. - PubMed
-
- McGrath J, Solter D. Completion of mouse embryogenesis requires both the maternal and paternal genomes. Cell. 1984;37:179–83. - PubMed
-
- Surani MA, Barton SC, Norris ML. Development of reconstituted mouse eggs suggests imprinting of the genome during gametogenesis. Nature. 1984;308:548–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
