KCNE1 constrains the voltage sensor of Kv7.1 K+ channels
- PMID: 18398469
- PMCID: PMC2275793
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001943
KCNE1 constrains the voltage sensor of Kv7.1 K+ channels
Abstract
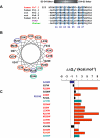
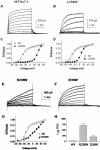
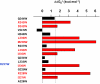
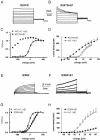
Kv7 potassium channels whose mutations cause cardiovascular and neurological disorders are members of the superfamily of voltage-gated K(+) channels, comprising a central pore enclosed by four voltage-sensing domains (VSDs) and sharing a homologous S4 sensor sequence. The Kv7.1 pore-forming subunit can interact with various KCNE auxiliary subunits to form K(+) channels with very different gating behaviors. In an attempt to characterize the nature of the promiscuous gating of Kv7.1 channels, we performed a tryptophan-scanning mutagenesis of the S4 sensor and analyzed the mutation-induced perturbations in gating free energy. Perturbing the gating energetics of Kv7.1 bias most of the mutant channels towards the closed state, while fewer mutations stabilize the open state or the inactivated state. In the absence of auxiliary subunits, mutations of specific S4 residues mimic the gating phenotypes produced by co-assembly of Kv7.1 with either KCNE1 or KCNE3. Many S4 perturbations compromise the ability of KCNE1 to properly regulate Kv7.1 channel gating. The tryptophan-induced packing perturbations and cysteine engineering studies in S4 suggest that KCNE1 lodges at the inter-VSD S4-S1 interface between two adjacent subunits, a strategic location to exert its striking action on Kv7.1 gating functions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
KCNE1 remodels the voltage sensor of Kv7.1 to modulate channel function.Biophys J. 2010 Dec 1;99(11):3599-608. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.10.018. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 21112284 Free PMC article.
-
KCNE1 and KCNE3 modulate KCNQ1 channels by affecting different gating transitions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Aug 29;114(35):E7367-E7376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1710335114. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28808020 Free PMC article.
-
S1 constrains S4 in the voltage sensor domain of Kv7.1 K+ channels.PLoS One. 2008 Apr 9;3(4):e1935. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001935. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18398461 Free PMC article.
-
KCNQ1 channel modulation by KCNE proteins via the voltage-sensing domain.J Physiol. 2015 Jun 15;593(12):2617-25. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.287672. Epub 2015 Feb 16. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25603957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hormonal Signaling Actions on Kv7.1 (KCNQ1) Channels.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021 Jan 6;61:381-400. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010919-023645. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 32667860 Review.
Cited by
-
KCNE1 remodels the voltage sensor of Kv7.1 to modulate channel function.Biophys J. 2010 Dec 1;99(11):3599-608. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.10.018. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 21112284 Free PMC article.
-
Location of KCNE1 relative to KCNQ1 in the I(KS) potassium channel by disulfide cross-linking of substituted cysteines.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jan 20;106(3):743-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811897106. Epub 2009 Jan 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19131515 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct subdomains of the KCNQ1 S6 segment determine channel modulation by different KCNE subunits.J Gen Physiol. 2009 Sep;134(3):207-17. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200910234. Epub 2009 Aug 17. J Gen Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19687231 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-Dependent Gating: Novel Insights from KCNQ1 Channels.Biophys J. 2016 Jan 5;110(1):14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.11.023. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 26745405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Working model for the structural basis for KCNE1 modulation of the KCNQ1 potassium channel.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2011 Apr;21(2):283-91. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2011.01.001. Epub 2011 Feb 4. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 21296569 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jentsch TJ. Neuronal KCNQ potassium channels: physiology and role in diseases. Nature Neurosci. 2000;1:21–30. - PubMed
-
- Robbins J. KCNQ potassium channels: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Ther. 2001;90:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Abbott GW, Goldstein SA. A superfamily of small potassium channel subunits: form and function of the MinK-related peptides (MiRPs). Q Rev Biophys. 1998;31:357–398. - PubMed
-
- Melman YF, Krummerman A, McDonald TV. KCNE regulation of KvLQT1 channels: structure-function correlates. Trends Cardiovascular Med. 2002;12:182–187. - PubMed
-
- Barhanin J, Lesage F, Guillemare E, Fink M, Lazdunski M, et al. KvLQT1 and lsK (minK) proteins associate to form the IKs cardiac potassium current [see comments]. Nature. 1996;384:78–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

