Long-term expression of murine activated factor VII is safe, but elevated levels cause premature mortality
- PMID: 18398505
- PMCID: PMC2289790
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32878
Long-term expression of murine activated factor VII is safe, but elevated levels cause premature mortality
Abstract
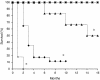
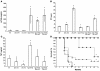
Intravenous infusion of recombinant human activated Factor VII (FVIIa) has been used for over a decade in the successful management of bleeding episodes in patients with inhibitory antibodies to Factor VIII or Factor IX. Previously, we showed that expression of murine FVIIa (mFVIIa) from an adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector corrected abnormal hemostatic parameters in hemophilia B mice. To pursue this as a therapeutic approach, we sought to define safe and effective levels of FVIIa for continuous expression. In mice transgenic for mFVIIa or injected with AAV-mFVIIa, we analyzed survival, expression levels, in vitro and in vivo coagulation tests, and histopathology for up to 16 months after birth/mFVIIa expression. We found that continuous expression of mFVIIa at levels at or below 1.5 microg/ml was safe, effective, and compatible with a normal lifespan. However, expression levels of 2 microg/ml or higher were associated with thrombosis and early mortality, with pathologic findings in the heart and lungs that were rescued in a low-factor X (low-FX) mouse background, suggesting a FX-mediated effect. The findings from these mouse models of continuous FVIIa expression have implications for the development of a safe gene transfer approach for hemophilia and are consistent with the possibility of thromboembolic risk of continuously elevated FVIIa levels.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Catalytic domain modification and viral gene delivery of activated factor VII confers hemostasis at reduced expression levels and vector doses in vivo.Blood. 2011 Apr 14;117(15):3974-82. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-309732. Epub 2011 Feb 16. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21325603 Free PMC article.
-
A novel therapeutic approach combining human plasma-derived Factors VIIa and X for haemophiliacs with inhibitors: evidence of a higher thrombin generation rate in vitro and more sustained haemostatic activity in vivo than obtained with Factor VIIa alone.Vox Sang. 2003 Nov;85(4):290-9. doi: 10.1111/j.0042-9007.2003.00365.x. Vox Sang. 2003. PMID: 14633255
-
One amino acid in mouse activated factor VII defines its endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) binding and modulates its EPCR-dependent hemostatic activity in vivo.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Mar;15(3):507-512. doi: 10.1111/jth.13607. Epub 2017 Feb 14. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28035745
-
Over-expression of factor VIIa in vivo.Thromb Res. 2008;122 Suppl 1:S70-2. doi: 10.1016/S0049-3848(08)70023-9. Thromb Res. 2008. PMID: 18691505 Review.
-
Potential role of recombinant factor VIIa as a hemostatic agent.Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2003 Feb;1(2):112-9. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2003. PMID: 16224390 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene-based FVIIa prophylaxis modulates the spontaneous bleeding phenotype of hemophilia A rats.Blood Adv. 2019 Feb 12;3(3):301-311. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018027219. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 30705032 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Delivery of Activated Factor VII Using Alternative Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype Improves Hemostasis in Hemophiliac Mice with FVIII Inhibitors and Adeno-Associated Virus Neutralizing Antibodies.Hum Gene Ther. 2017 Aug;28(8):654-666. doi: 10.1089/hum.2017.016. Epub 2017 May 5. Hum Gene Ther. 2017. PMID: 28478688 Free PMC article.
-
Employing a gain-of-function factor IX variant R338L to advance the efficacy and safety of hemophilia B human gene therapy: preclinical evaluation supporting an ongoing adeno-associated virus clinical trial.Hum Gene Ther. 2015 Feb;26(2):69-81. doi: 10.1089/hum.2014.106. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Hum Gene Ther. 2015. PMID: 25419787 Free PMC article.
-
FVIIa as used pharmacologically is not TF dependent in hemophilia B mice.Blood. 2014 Mar 13;123(11):1764-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-08-522987. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24425804 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocapsule-delivered Sleeping Beauty mediates therapeutic Factor VIII expression in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells of hemophilia A mice.J Clin Invest. 2009 Jul;119(7):2086-99. doi: 10.1172/JCI34332. Epub 2009 Jun 8. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19509468 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ingerslev J., et al. Major surgery in haemophilic patients with inhibitors using recombinant factor VIIa. Haemostasis. 1996;26(Suppl. 1):118–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

