Exercise alters the immune profile in Tg2576 Alzheimer mice toward a response coincident with improved cognitive performance and decreased amyloid
- PMID: 18400101
- PMCID: PMC2329612
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-13
Exercise alters the immune profile in Tg2576 Alzheimer mice toward a response coincident with improved cognitive performance and decreased amyloid
Abstract
Background: Inflammation is associated with Abeta pathology in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and transgenic AD models. Previously, it has been demonstrated that chronic stimulation of the immune response induces pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1beta and TNF-alpha which contribute to neurodegeneration. However, recent evidence has shown that inducing the adaptive immune response reduces Abeta pathology and is neuroprotective. Low concentrations of IFN-gamma modulate the adaptive immune response by directing microglia to differentiate to antigen presenting cells. Our objective was to determine if exercise could induce a shift from the immune profile in aged (17-19 months) Tg2576 mice to a response that reduces Abeta pathology.
Methods: TG (n = 29) and WT (n = 27) mice were divided into sedentary (SED) and exercised (RUN) groups. RUN animals were provided an in-cage running wheel for 3 weeks. Tissue was harvested and hippocampus and cortex dissected out. Quantitative data was analyzed using 2 x 2 ANOVA and student's t-tests.
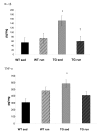
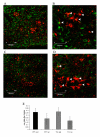
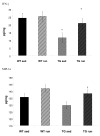
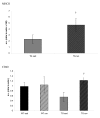
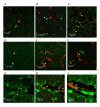
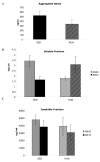
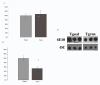
Results: IL-1beta and TNF-alpha were significantly greater in hippocampi from sedentary Tg2576 (TGSED) mice than in wildtype (WTSED) (p = 0.04, p = 0.006). Immune response proteins IFN-gamma and MIP-1alpha are lower in TGSED mice than in WTSED (p = 0.03, p = 0.07). Following three weeks of voluntary wheel running, IL-1beta and TNF-alpha decreased to levels indistinguishable from WT. Concurrently, IFN-gamma and MIP-1alpha increased in TGRUN. Increased CD40 and MHCII, markers of antigen presentation, were observed in TGRUN animals compared to TGSED, as well as CD11c staining in and around plaques and vasculature. Additional vascular reactivity observed in TGRUN is consistent with an alternative activation immune pathway, involving perivascular macrophages. Significant decreases in soluble Abeta40 (p = 0.01) and soluble fibrillar Abeta (p = 0.01) were observed in the exercised transgenic animals.
Conclusion: Exercise shifts the immune response from innate to an adaptive or alternative response. This shift in immune response coincides with a decrease in Abeta in advanced pathological states.
Figures
References
-
- Dishman RK, Berthoud HR, Booth FW, Cotman CW, Edgerton VR, Fleshner MR, Gandevia SC, Gomez-Pinilla F, Greenwood BN, Hillman CH, Kramer AF, Levin BE, Moran TH, Russo-Neustadt AA, Salamone JD, Van Hoomissen JD, Wade CE, York DA, Zigmond MJ. Neurobiology of exercise. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2006;14:345–356. - PubMed
-
- Larson EB, Wang L, Bowen JD, McCormick WC, Teri L, Crane P, Kukull W. Exercise is associated with reduced risk for incident dementia among persons 65 years of age and older. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:73–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

