A bioluminescent cytotoxicity assay for assessment of membrane integrity using a proteolytic biomarker
- PMID: 18400464
- PMCID: PMC2386563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2008.02.013
A bioluminescent cytotoxicity assay for assessment of membrane integrity using a proteolytic biomarker
Abstract
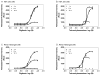
Measurement of cell membrane integrity has been widely used to assess chemical cytotoxity. Several assays are available for determining cell membrane integrity including differential labeling techniques using neutral red and trypan blue dyes or fluorescent compounds such as propidium iodide. Other common methods for assessing cytotoxicity are enzymatic "release" assays which measure the extra-cellular activities of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), adenylate kinase (AK), or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in culture medium. However, all these assays suffer from several practical limitations, including multiple reagent additions, scalability, low sensitivity, poor linearity, or requisite washes and medium exchanges. We have developed a new cytotoxicity assay which measures the activity of released intracellular proteases as a result of cell membrane impairment. It allows for a homogenous, one-step addition assay with a luminescent readout. We have optimized and miniaturized this assay into a 1536-well format, and validated it by screening a library of known compounds from the National Toxicology Program (NTP) using HEK 293 and human renal mesangial cells by quantitative high-throughput screening (qHTS). Several known and novel membrane disrupters were identified from the library, which indicates that the assay is robust and suitable for large scale library screening. This cytotoxicity assay, combined with the qHTS platform, allowed us to quickly and efficiently evaluate compound toxicities related to cell membrane integrity.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson BM, Noble C., Jr In vitro inhibition of lactate dehydrogenases by kepone. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 1977;25:28–31. - PubMed
-
- Blonder E, Klibansky C, DE Vries A. Effects of detergents and choline-containing phospholipids on human spleen glucocerebrosidase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1976;431:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Boisclar M, Iwata K. HTS using cell-based assays for drug discovery. Am Assoc Cancer Res Educ Book. 2005 April 2005;:363–368.
-
- Corey MJ, Kinders R, Brown L, Vessella R. A very sensitive coupled luminescent assay for cytotoxicity and complement-mediated lysis. Journal of Immunological Methods. 1997;207:43–51. - PubMed
-
- Digan ME, Pou C, Niu H, Zhang J. Evaluation of division-arrested cells for cell-based high throughput screening profiling. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 2005;10:615–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

