Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: molecular mechanisms of action during steady state and 'emergency' hematopoiesis
- PMID: 18400509
- PMCID: PMC2852428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.03.002
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: molecular mechanisms of action during steady state and 'emergency' hematopoiesis
Abstract
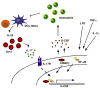
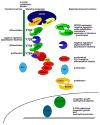
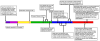
Neutrophils are phagocytes whose principal function is to maintain anti-bacterial immunity. Neutrophils ingest and kill invading bacteria, releasing cytotoxic, chemotactic and inflammatory mediators at sites of infection. This serves to control the immediate host immune response and attract other cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, which are important for establishing long-term adaptive immunity. Neutrophils thus contribute to both the initiation and the maintenance of inflammation at sites of infection. Aberrant neutrophil activity is deleterious; suppressed responses can cause extreme susceptibility to infection while overactivation can lead to excessive inflammation and tissue damage. This review will focus on neutrophil regulation by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), the principal cytokine controlling neutrophil development and function. The review will emphasize the molecular aspects of G-CSF-driven granulopoiesis in steady state (healthy) conditions and during demand-driven or 'emergency' conditions elicited by infection or clinical administration of G-CSF. Understanding the molecular control of granulopoiesis will aid in the development of new approaches designed to treat disorders of neutrophil production and function.
Figures
References
-
- Huising MO, Kruiswijk CP, Flik G. Phylogeny and evolution of class-I helical cytokines. J Endocrinol. 2006;189:1–25. - PubMed
-
- Lutfalla G, Roest Crollius H, Stange-Thomann N, Jaillon O, Mogensen K, Monneron D. Comparative genomic analysis reveals independent expansion of a lineage-specific gene family in vertebrates: the class II cytokine receptors and their ligands in mammals and fish. BMC Genomics. 2003;4:29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lieschke GJ, Grail D, Hodgson G, Metcalf D, Stanley E, Cheers C, Fowler KJ, Basu S, Zhan YF, Dunn AR. Mice lacking granulocyte colony-stimulating factor have chronic neutropenia, granulocyte and macrophage progenitor cell deficiency, and impaired neutrophil mobilization. Blood. 1994;84:1737–46. - PubMed
-
- Zeidler C, Schwinzer B, Welte K. Congenital neutropenias. Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2003;7:72–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

