A randomized study of extended dosing regimens for initiation of epoetin alfa treatment for anemia of chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 18400964
- PMCID: PMC2440274
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05681207
A randomized study of extended dosing regimens for initiation of epoetin alfa treatment for anemia of chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: Although epoetin alfa is commonly initiated weekly (QW) in anemic chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients, recent evidence indicates that it can be initiated every 2 wk (Q2W) and used in maintenance therapy every 4 wk (Q4W). This study examined the feasibility of initiating epoetin alfa Q4W in anemic CKD patients not receiving dialysis.
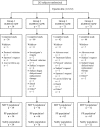
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: This open-label study randomized subjects (1:2:2:2) to treatment with epoetin alfa 10,000 IU QW, 20,000 IU Q2W, 20,000 IU Q4W, or 40,000 IU Q4W for 16 wk. Subjects were > or =18 yr, had hemoglobin <11 g/dl, a glomerular filtration rate of 15 to 90 ml/min per 1.73 m(2), and had not received erythropoietic therapy within 8 wk. The primary analysis was a noninferiority comparison of the 40,000 IU Q4W to the 20,000 IU Q2W group in the per-protocol population with respect to hemoglobin change from baseline to the end of study.
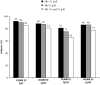
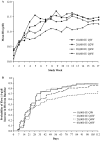
Results: Of 262 subjects randomized, 229 comprised the per-protocol population. Mean hemoglobin change from baseline for the 40,000 IU Q4W group (1.24 g/dl) was not inferior to the 20,000 IU Q2W group (1.11 g/dl) with the lower limit of 95% CI, -0.21 g/dl. In the QW, 20,000 IU Q2W, 20,000 IU Q4W, and 40,000 IU Q4W groups, 90%, 87%, 75%, and 86% of subjects, respectively, achieved a hemoglobin increase > or =1 g/dl. Serious adverse events were similar across all groups.
Conclusions: Epoetin alfa can be initiated Q4W in anemic CKD subjects.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00212875.
Figures
Comment in
-
Erythropoietin stimulating agents and epoetin alfa revisited: what's really relevant?Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Jul;3(4):935-7. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02300508. Epub 2008 Jun 25. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18579671 No abstract available.
References
-
- Richter A, Anton SE, Koch P, Dennett SL: The impact of reducing dose frequency on health outcomes. Clin Ther 25: 2307–2335, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Germain M, Ram CV, Bhaduri S, Tang KL, Klausner M, Curzi M: Extended epoetin alfa dosing in chronic kidney disease patients: a retrospective review. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20: 2146–2152, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Piccoli A, Malagoli A, Komninos G, Pastori G: Subcutaneous epoetin-alpha every one, two, and three weeks in renal anemia. J Nephrol 15: 565–574, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Provenzano R, Bhaduri S, Singh AK: Extended epoetin alfa dosing as maintenance treatment for the anemia of chronic kidney disease: the PROMPT study. Clin Nephrol 64: 113–123, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Benz R, Schmidt R, Kelly K, Wolfson M: Epoetin alfa once every 2 weeks is effective for initiation of treatment of anemia of chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2: 215–221, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

