A cluster randomized trial to evaluate physician/pharmacist collaboration to improve blood pressure control
- PMID: 18401223
- PMCID: PMC2453045
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2008.07434.x
A cluster randomized trial to evaluate physician/pharmacist collaboration to improve blood pressure control
Abstract
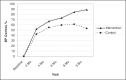
This was a prospective, cluster randomized controlled trial in patients with uncontrolled hypertension aged 21 to 85 years (mean, 61 years). Pharmacists made recommendations to physicians for patients in the intervention clinics (n=101) but not patients in the control clinics (n=78). The mean adjusted difference in systolic blood pressure (BP) between the control and intervention groups was 8.7 mm Hg (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.4-12.9), while the difference in diastolic BP was 5.4 mm Hg (CI, 2.8-8.0) at 9 months. The 24-hour BP levels showed similar effects, with a mean systolic BP level that was 8.8 mm Hg lower (CI, 5.0-12.6) and a mean diastolic BP level that was 4.6 mm Hg (CI, 2.4-6.8) lower in the intervention group. BP was controlled in 89.1% of patients in the intervention group and 52.9% in the control group (adjusted odds ratio, 8.9; CI, 3.8-20.7; P<.001). Physician/pharmacist collaboration achieved significantly better mean BP values and overall BP control rates, primarily by intensification of medication therapy and improving patient adherence.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00201045.
Figures

References
-
- European Society of Hypertension‐European Society of Cardiology Guidelines Committee . 2003 European Society of Hypertension‐European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens. 2003;21(6):1011–1053. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Report 2002–Reducing Risks, Promoting Healthy Life. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2002.http://www.who.int/whr/2002/. Accessed December 26, 2006.
-
- Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42(6):1206–1252. - PubMed
-
- Garg JP, Elliott WJ, Folker A, et al. Resistant hypertension revisited: a comparison of two university‐based cohorts. Am J Hypertens. 2005;18(5, pt 1):619–626. - PubMed
-
- Berlowitz DR, Ash AS, Hickey EC, et al. Inadequate management of blood pressure in a hypertensive population. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(27):1957–1963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

