Human Delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase: function and regulation
- PMID: 18401542
- PMCID: PMC2707934
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-008-0075-0
Human Delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase: function and regulation
Abstract
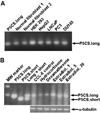
Mammalian Delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase (P5CS) is a bifunctional ATP- and NAD(P)H-dependent mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the coupled phosphorylation and reduction-conversion of L: -glutamate to P5C, a pivotal step in the biosynthesis of L: -proline, L: -ornithine and L: -arginine. Previously, we reported cloning and characterization of two P5CS transcript variants generated by exon sliding that encode two protein isoforms differing only by a two amino acid-insert at the N-terminus of the gamma-glutamyl kinase active site. The short form (P5CS.short) is highly expressed in the gut and is inhibited by ornithine. In contrast, the long form (P5CS.long) is expressed ubiquitously and is insensitive to ornithine. Interestingly, we found that all the established human cell lines we have studied expressed P5CS.long but not P5CS.short. In addition, expression of P5CS.long can be modulated by hormones: downregulation by hydrocortisone and dexamethasone and upregulation by estradiol, for example. Using a quantitative proteomic approach, we showed that P5CS.long is upregulated by p53 in p53-induced apoptosis in DLD-1 colorectal cancer cells. Functional genomic analysis confirmed that there are two p53-binding consensus sequences in the promoter region and in the intron 1 of the human P5CS gene. Interestingly, overexpression of P5CS by adenoviruses harboring P5CS.long or P5CS.short in various cell types has no effect on cell growth or survival. It would be of importance to further investigate the role of P5CS as a p53 downstream effector and how P5CS.short expression is regulated by hormones and factors of alternative splicing in cells isolated from model animals.
Figures




References
-
- Adhani VM, Ahmad N, Kukhtar H. Molecular targets for green tea in prostate cancer prevention. J Nutr. 2003;133:2417S–2424S. - PubMed
-
- Adams E, Frank L. Metabolism of proline and the hydroxyproline. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1005–1061. - PubMed
-
- Aral B, Schlenzig JS, Liu G, Kamoun P. Database cloning human delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS) cDNA: a bifunctional enzyme catalyzing the first 2 steps in proline biosynthesis. C R Acad Sci III. 1996;319:171–178. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner MR, Aral B, Rabier D, Kamoun P, Valle D, Saudubray J-M. Hyperammonemia with reduced ornithine, citrulline, arginine and proline: a new inborn error caused by a mutation in the gene encoding delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase. Eur J Pediatr. 2005;164:31–36. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner MR, Hu CAA, Almashanu S, Steel G, Obie C, Aral B, Rabier D, Kamoun P, Saudubray J-M, Valle D. Hyperammonemia with reduced ornithine, citrulline, arginine and proline: a new inborn error caused by a mutation in the gene encoding delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase. Hum Mol Gen. 2000;9:2853–2858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

