Delivery of recombinant adeno-associated virus-mediated human tissue kallikrein for therapy of chronic renal failure in rats
- PMID: 18402547
- PMCID: PMC2376255
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2007.138
Delivery of recombinant adeno-associated virus-mediated human tissue kallikrein for therapy of chronic renal failure in rats
Abstract
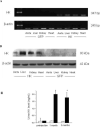
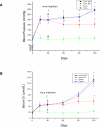
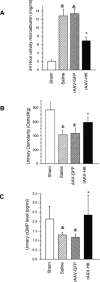
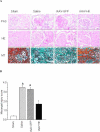
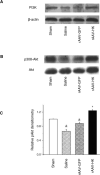
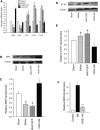
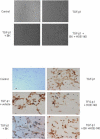
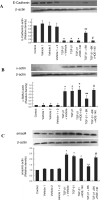
The tissue kallikrein-kinin system is important in regulating cardiovascular and renal function, and dysregulation of the system has been implicated in heart and kidney pathologies. These findings suggest that if balance can be restored to the kallikrein-kinin axis, then associated disease progression may be attenuated. To test this hypothesis, recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV)-mediated human tissue kallikrein (HK) expression was induced in a rodent model of chronic renal failure involving 5/6 nephrectomy (nephrectomy plus 70% reduction of remaining kidney). rAAV-HK treatment attenuated the rise in blood pressure, glomerular sclerosis, and tubulointerstitial injury observed in this model. rAAV-HK treatment also attenuated renal function decline as measured by urinary microalbumin, osmolarity, and cGMP levels. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis showed that rAAV-HK-treated rats had higher levels of bradykinin receptor-2 (B(2)R) and dopamine receptor-1 mRNAs. In contrast, angiotensin II receptor-1, endothelin receptor-A, and vasopressin receptor-2 mRNAs were markedly downregulated in kidneys from HK-treated rats. Bradykinin induced similar changes in receptor levels and prevented transforming growth factor-beta(1)-induced tubulointerstitial fibrosis. The effects of bradykinin could be reversed with the B(2)R antagonist HOE-140. Together, these findings suggest that restoration of the kallikrein-kinin system reduces kidney injury and protects renal function in 5/6-nephrectomized rats via changes in the expression and activation of G protein-coupled receptors including B(2)R.
Figures

References
-
- Moeller S, Gioberge S, Brown G. ESRD patients in 2001: global overview of patients, treatment modalities and development trends. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002;17(12):2071–2076. - PubMed
-
- Xue JL, et al. Forecast of the Number of Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States to the Year 2010. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12(12):2753–2758. - PubMed
-
- Scicli AG, C.O. Renal kallikrein-kinin system. Kidney Int. 1986;29(1):120–130. - PubMed
-
- Margolius HS. Tissue kallikreins and kinins: regulation and roles in hypertensive and diabetic diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:343–64. - PubMed
-
- Margolius HS, et al. Urinary kallikrein excretion in hypertensive man. Relationships to sodium intake and sodium-retaining steroids. Circ Res. 1974;35(6):820–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

