Locomotor stimulation produced by 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) is correlated with dialysate levels of serotonin and dopamine in rat brain
- PMID: 18403002
- PMCID: PMC2491560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.02.018
Locomotor stimulation produced by 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) is correlated with dialysate levels of serotonin and dopamine in rat brain
Abstract
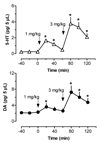
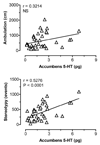
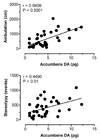
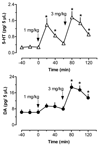
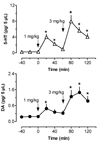
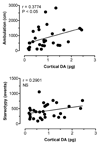
(+/-)-3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, or Ecstasy) is an illicit drug that evokes transporter-mediated release of monoamines, including serotonin (5-HT) and dopamine (DA). Here we monitored the effects of MDMA on neurochemistry and motor activity in rats, as a means to evaluate relationships between 5-HT, DA, and behavior. Male rats undergoing in vivo microdialysis were housed in chambers equipped with photobeams for measurement of ambulation (i.e., forward locomotion) and stereotypy (i.e., head weaving and forepaw treading). Microdialysis probes were placed into the n. accumbens, striatum or prefrontal cortex in separate groups of rats. Dialysate samples were assayed for 5-HT and DA by microbore HPLC-ECD. Rats received two i.v. injections of MDMA, 1 mg/kg followed by 3 mg/kg 60 min later; neurochemical and locomotor parameters were measured concurrently. MDMA produced dose-related elevations in extracellular 5-HT and DA in all regions, with the magnitude of 5-HT release always exceeding that of DA release. MDMA-induced ambulation was positively correlated with dialysate DA levels in all regions (P<0.05-0.0001) and with dialysate 5-HT in striatum and cortex (P<0.001-0.0001). Stereotypy was strongly correlated with dialysate 5-HT in all areas (P<0.001-0.0001) and with dialysate DA in accumbens and striatum (P<0.001-0.0001). These data support previous work and suggest the complex spectrum of behaviors produced by MDMA involves 5-HT and DA in a region- and modality-specific manner.
Figures




References
-
- Amalric M, Koob GF. Functionally selective neurochemical afferents and efferents of the mesocorticolimbic and nigrostriatal dopamine system. Prog Brain Res. 1993;99:209–226. - PubMed
-
- Andrews CD, Fernando JC, Curzon G. Differential involvement of dopamine-containing tracts in 5-hydroxytryptamine-dependent behaviours caused by amphetamine in large doses. Neuropharmacology. 1982;21:63–68. - PubMed
-
- Ball KT, Budreau D, Rebec GV. Acute effects of 3,4- methylenedioxymethamphetamine on striatal single-unit activity and behavior in freely moving rats: differential involvement of dopamine D(1) and D(2) receptors. Brain Res. 2003;994:203–215. - PubMed
-
- Ball KT, Rebec GV. Role of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C/B receptors in the acute effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on striatal single-unit activity and locomotion in freely moving rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005;181:676–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

