Increased IL-23 secretion and altered chemokine production by dendritic cells upon CD46 activation in patients with multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 18403025
- PMCID: PMC2702859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.01.002
Increased IL-23 secretion and altered chemokine production by dendritic cells upon CD46 activation in patients with multiple sclerosis
Abstract
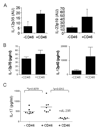
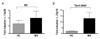
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS). In MS, myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) secrete elevated amounts of IL-23, a potent proinflammatory cytokine, compared to healthy donors. Here, we examined the role of CD46, a complement binding factor, in mDCs by analyzing cytokine and chemokine production in healthy donors and patients with MS. There were striking differences between these groups with increased IL-23p19, CCL3 and CCL5 production, but decreased CCL2 levels in patients. This demonstrates major differences of DC activation upon CD46 activation, with a potential role in the pathogenesis of MS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Myeloid dendritic cells exhibit defects in activation and function in patients with multiple sclerosis.J Neuroimmunol. 2016 Dec 15;301:53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Nov 2. J Neuroimmunol. 2016. PMID: 27836182
-
Vitamin D/CD46 Crosstalk in Human T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 24;11:598727. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.598727. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33329593 Free PMC article.
-
IL-23 is increased in dendritic cells in multiple sclerosis and down-regulation of IL-23 by antisense oligos increases dendritic cell IL-10 production.J Immunol. 2006 Jun 15;176(12):7768-74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.12.7768. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16751425
-
CD46 plasticity and its inflammatory bias in multiple sclerosis.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2011 Feb;59(1):49-59. doi: 10.1007/s00005-010-0109-7. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2011. PMID: 21267793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-cell regulation by CD46 and its relevance in multiple sclerosis.Immunology. 2008 Jun;124(2):149-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02821.x. Epub 2008 Apr 2. Immunology. 2008. PMID: 18384356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting aryl hydrocarbon receptor functionally restores tolerogenic dendritic cells derived from patients with multiple sclerosis.J Clin Invest. 2024 Nov 1;134(21):e178949. doi: 10.1172/JCI178949. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39287981 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk pathways between Toll-like receptors and the complement system.Trends Immunol. 2010 Apr;31(4):154-63. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2010.01.002. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Trends Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20153254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H(1)R expression by CD11B(+) cells is not required for susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis.Cell Immunol. 2012 Jul-Aug;278(1-2):27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2012.06.012. Epub 2012 Jul 14. Cell Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23121973 Free PMC article.
-
CD46 in innate and adaptive immunity: an update.Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 Jun;164(3):301-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04400.x. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21488871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of neuroinflammation: enhanced cytotoxicity and IL-17 production via CD46 binding.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;5(3):469-78. doi: 10.1007/s11481-010-9232-9. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20661655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adorini L. Immunotherapeutic approaches in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2004;223:13–24. - PubMed
-
- Astier A, Trescol-Biemont MC, Azocar O, Lamouille B, Rabourdin-Combe C. Cutting edge: CD46, a new costimulatory molecule for T cells, that induces p120CBL and LAT phosphorylation. J Immunol. 2000;164:6091–6095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

