Increased IL-23 secretion and altered chemokine production by dendritic cells upon CD46 activation in patients with multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 18403025
- PMCID: PMC2702859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.01.002
Increased IL-23 secretion and altered chemokine production by dendritic cells upon CD46 activation in patients with multiple sclerosis
Abstract
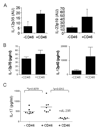
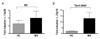
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS). In MS, myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) secrete elevated amounts of IL-23, a potent proinflammatory cytokine, compared to healthy donors. Here, we examined the role of CD46, a complement binding factor, in mDCs by analyzing cytokine and chemokine production in healthy donors and patients with MS. There were striking differences between these groups with increased IL-23p19, CCL3 and CCL5 production, but decreased CCL2 levels in patients. This demonstrates major differences of DC activation upon CD46 activation, with a potential role in the pathogenesis of MS.
Figures

References
-
- Adorini L. Immunotherapeutic approaches in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2004;223:13–24. - PubMed
-
- Astier A, Trescol-Biemont MC, Azocar O, Lamouille B, Rabourdin-Combe C. Cutting edge: CD46, a new costimulatory molecule for T cells, that induces p120CBL and LAT phosphorylation. J Immunol. 2000;164:6091–6095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

