OutFOXOing disease and disability: the therapeutic potential of targeting FoxO proteins
- PMID: 18403263
- PMCID: PMC2572150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2008.03.002
OutFOXOing disease and disability: the therapeutic potential of targeting FoxO proteins
Abstract
Forkhead transcription factors have a 'winged helix' domain and regulate processes that range from cell longevity to cell death. Of the mammalian forkhead family members in the O class, FoxO1, FoxO3a and FoxO4 can fill a crucial void for the treatment of disorders that include aging, cancer, diabetes, infertility, neurodegeneration and immune system dysfunction. Yet, observations that forkhead family members also can compromise clinical utility have fueled controversy and highlight the necessity to further outline the integrated cellular pathways governed by these transcription factors. Here we discuss recent advances that have elucidated the unique cellular pathways and clinical potential of targeting FoxO proteins to develop novel therapeutic strategies and avert potential pitfalls that might be closely intertwined with its benefits for patient care.
Figures
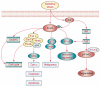
References
-
- Chong ZZ, et al. Oxidative stress in the brain: novel cellular targets that govern survival during neurodegenerative disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005;75:207–246. - PubMed
-
- Hoekman MF, et al. Spatial and temporal expression of FoxO transcription factors in the developing and adult murine brain. Gene Expr. Patterns. 2006;6:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Myatt SS, Lam EW. The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2007;7:847–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

