Interleukin-4 activates large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium (BKCa) channels in human airway smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 18403443
- PMCID: PMC4115791
- DOI: 10.1113/expphysiol.2008.042432
Interleukin-4 activates large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium (BKCa) channels in human airway smooth muscle cells
Abstract
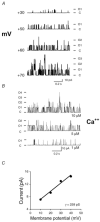
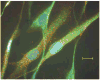
Large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium (BK(Ca)) channels are regulated by voltage and near-membrane calcium concentrations and are determinants of membrane potential and excitability in airway smooth muscle cells. Since the T helper-2 (Th2) cytokine, interleukin (IL)-4, is an important mediator of airway inflammation, we investigated whether IL-4 rapidly regulated BK(Ca) activity in normal airway smooth muscle cells. On-cell voltage clamp recordings were made on subconfluent, cultured human bronchial smooth muscle cells (HBSMC). Interleukin-4 (50 ng ml(-1)), IL-13 (50 ng ml(-1)) or histamine (10 microm) was added to the bath during the recordings. Immunofluorescence studies with selective antibodies against the alpha and beta1 subunits of BK(Ca) were also performed. Both approaches demonstrated that HBSMC membranes contained large-conductance channels (>200 pS) with both calcium and voltage sensitivity, all of which is characteristic of the BK(Ca) channel. Histamine caused a rapid increase in channel activity, as expected. A new finding was that perfusion with IL-4 stimulated rapid, large increases in BK(Ca) channel activity (77.2 +/- 63.3-fold increase, P < 0.05, n = 18). This large potentiation depended on the presence of external calcium. In contrast, IL-13 (50 ng ml(-1)) had little effect on BK(Ca) channel activity, but inhibited the effect of IL-4. Thus, HBSMC contain functional BK(Ca) channels whose activity is rapidly potentiated by the cytokine, IL-4, but not by IL-13. These findings are consistent with a model in which IL-4 rapidly increases near-membrane calcium concentrations to regulate BK(Ca) activity.
Figures


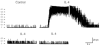


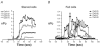

Similar articles
-
Local Ca(2+) transients and distribution of BK channels and ryanodine receptors in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig vas deferens and urinary bladder.J Physiol. 2001 Jul 15;534(Pt. 2):313-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.t01-3-00313.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11454953 Free PMC article.
-
Bradykinin activates calcium-dependent potassium channels in cultured human airway smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007 Apr;292(4):L898-907. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00461.2005. Epub 2006 Dec 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17158598
-
Mechanism of beta4 subunit modulation of BK channels.J Gen Physiol. 2006 Apr;127(4):449-65. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200509436. J Gen Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16567466 Free PMC article.
-
Large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels: structural and functional implications.Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Apr;110(1):103-16. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.10.007. Epub 2005 Dec 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16356551 Review.
-
Multiple regulatory effects of angiotensin II on the large-conductance Ca2+- and voltage-activated potassium channel in vascular smooth muscle cells.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2019 Apr 25;71(2):187-195. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31008478 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-4 inhibits calcium transients in bovine trachealis cells by a ryanodine receptor-dependent mechanism.FASEB J. 2006 Jan;20(1):154-6. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-4031fje. Epub 2005 Nov 9. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16280365 Free PMC article.
-
IL-4 deficiency is associated with mechanical hypersensitivity in mice.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28205. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028205. Epub 2011 Dec 2. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22164245 Free PMC article.
-
A C. elegans Model for the Study of RAGE-Related Neurodegeneration.Neurotox Res. 2019 Jan;35(1):19-28. doi: 10.1007/s12640-018-9918-y. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 29869225
-
Bitter taste receptors on airway smooth muscle bronchodilate by localized calcium signaling and reverse obstruction.Nat Med. 2010 Nov;16(11):1299-304. doi: 10.1038/nm.2237. Epub 2010 Oct 24. Nat Med. 2010. PMID: 20972434 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MicroRNA in the Airway Surface Liquid Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 28;21(11):3848. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113848. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32481719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bamford TL, Guida E, Harris ET, Wilson JW, Nash A, Stewart AG. IL-13 activates human cultured airway smooth muscle through the IL-13Ra1 receptor. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:A599.
-
- Cooper S. Reappraisal of serum starvation, the restriction point, G0, and G1 phase arrest points. FASEB J. 2003;17:333–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

