Role of TRPV1 channels in renal haemodynamics and function in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats
- PMID: 18403445
- PMCID: PMC2693710
- DOI: 10.1113/expphysiol.2008.042036
Role of TRPV1 channels in renal haemodynamics and function in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats
Abstract
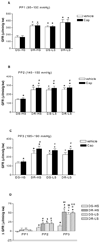
This study tests the hypothesis that dysfunction of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channels occurs and contributes to the decrease in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and sodium/water excretion in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Recirculating Krebs-Henseleit buffer added with inulin was perfused at a constant flow in the isolated kidneys of Dahl salt-sensitive (DS) or Dahl salt-resistant (DR) rats fed a high-salt (HS) or low-salt (LS) diet for 3 weeks. Perfusion pressures (PP) were pre-adjusted to three levels ( approximately 100, approximately 150 or approximately 190 mmHg) with or without phenylephrine. Capsaicin, a selective TRPV1 agonist, in the presence or absence of capsazepine, a selective TRPV1 antagonist, was perfused. Basal GFR, urine flow rate (UFR) and Na(+) excretion (U(Na)V) were significantly lower in DS-HS than in DR-HS, DS-LS and DR-LS rats. Capsaicin caused pressure-dependent decreases in PP and increases in GFR, UFR and U(Na)V in all groups, with less magnitude of decreases in PP and increases in GFR, UFR and U(Na)V in DS-HS than in DR-HS, DS-LS and DR-LS rats. Capsazepine completely blocked the effect of capsaicin on PP, GFR, UFR and U(Na)V in all groups. Thus, these results show that TRPV1 function is impaired in the kidney of DS rats fed a high-salt diet, which may contribute to the decrease in GFR and renal excretory function in DS rats in the face of salt challenge.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Increased GFR and renal excretory function by activation of TRPV1 in the isolated perfused kidney.Pharmacol Res. 2008 Mar;57(3):239-46. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2008.01.011. Epub 2008 Feb 2. Pharmacol Res. 2008. PMID: 18329285 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mechanism contributing to development of Dahl salt-sensitive hypertension: role of the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1.Hypertension. 2006 Mar;47(3):609-14. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000197390.10412.c4. Epub 2005 Dec 19. Hypertension. 2006. PMID: 16365187
-
Impairment in function and expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 4 in Dahl salt-sensitive rats: significance and mechanism.Hypertension. 2010 Apr;55(4):1018-25. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.147710. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Hypertension. 2010. PMID: 20194297 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a high-salt diet on TRPV-1-dependent renal nerve activity in Dahl salt-sensitive rats.Am J Nephrol. 2010;32(3):194-200. doi: 10.1159/000316528. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Am J Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20639627 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium entry modulation and renal hemodynamics in the hypertensive kidney.Am J Nephrol. 1987;7 Suppl 1:17-23. doi: 10.1159/000167538. Am J Nephrol. 1987. PMID: 2450458 Review.
Cited by
-
The Vanilloid (Capsaicin) Receptor TRPV1 in Blood Pressure Regulation: A Novel Therapeutic Target in Hypertension?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 15;24(10):8769. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108769. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid channels in hypertension, inflammation, and end organ damage: an imminent target of therapy for cardiovascular disease?Curr Opin Cardiol. 2008 Jul;23(4):356-63. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0b013e32830460ad. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18520720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of transient receptor potential channels in the regulation of vascular tone.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Jul;29(7):104051. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.104051. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 38838960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Periglomerular afferent innervation of the mouse renal cortex.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jan 26;17:974197. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.974197. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36777644 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Chronic Administration of Capsaicin on Biomarkers of Kidney Injury in Male Wistar Rats with Experimental Diabetes.Molecules. 2018 Dec 21;24(1):36. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010036. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30583465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amuchastegui CS, Remuzzi G, Perico N. Calcitonin gene-related peptide reduces renal vascular resistance and modulates ET-1-induced vasoconstriction. AM J Physiol. 1994;267(5 Pt 2):F839–F844. - PubMed
-
- Campese VM. Salt sensitivity in hypertension: renal and cardiovascular implications. Hypertension. 1994;23:531, 550. - PubMed
-
- Caterina MJ, Julius D. The vanilloid receptor: a molecular gate-way to the pain pathway. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:487, 517. - PubMed
-
- Cowley AW, Jr, Roman RJ. The role of the kidney in hypertension. JAMA. 1996;275:1581, 1589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

