Signaling pathways for B cell-activating factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) in human placenta
- PMID: 18403603
- PMCID: PMC2329839
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.071139
Signaling pathways for B cell-activating factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) in human placenta
Abstract
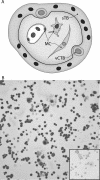
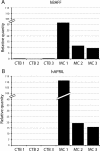
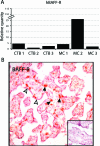
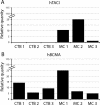
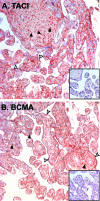
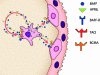
The tumor necrosis superfamily (TNFSF) contains two soluble ligands that are involved in B lymphocyte development, BAFF (B cell activating factor, BlyS, TALL-1, CD257, TNFSF13B) and APRIL (a proliferation inducing ligand, CD256, TNFSF13). These two ligands signal through three receptors: the exclusive BAFF receptor (BAFF-R, CD268, TNFRSF17) and two receptors that recognize both BAFF and APRIL, TACI (transmembrane-activator-1 and calcium-modulator- and cyclophilin ligand-interactor CD267, TNFRSF13B) and BCMA (B cell maturation antigen, CD269, TNFRSF13C). All but BAFF-R are known to be synthesized in term placentas. In this study, expression of the ligands and receptors were distinguished in two embryologically discrete subpopulations of placental cells, villous cytotrophoblast (vCTB) cells and mesenchymal cells (MCs). Real-Time PCR showed that vCTB cells contain low levels of BAFF and APRIL transcripts whereas MCs contain high levels. Both Real-Time PCR and immunohistochemistry identified BAFF-R and BCMA mRNA and proteins in vCTB cells but essentially no TACI. By contrast, MCs contained readily detectable levels of all three receptors. These results illustrating potential autocrine and paracrine pathways for BAFF and APRIL signaling in human placentas suggest that lineage-specific regulation of placental cell viability, differentiation and/or other activities may be novel functions of these proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Hunt JS, Chen HL, Miller L. Tumor necrosis factors: pivotal factors in pregnancy? Biol Reprod. 1996;54:554–562. - PubMed
-
- Phillips TA, Ni J, Hunt JS. Death-inducing tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily ligands and receptors are transcribed in human placentas. CTBs, placental macrophages and placental cell lines. Placenta. 2001;22:663–672. - PubMed
-
- Phillips TA, Ni J, Hunt JS. Cell-specific expression of B lymphocyte- (APRIL. BLyS) and Th2- (CD30L/CD153) promoting tumor necrosis factor superfamily ligands in human placentas. J Leukocyte Biol. 2003;74:81–87. - PubMed
-
- Moore PA, Belvedere O, Orr A, Pier K, LaFleur DW, Feng P, Soppet D, Charters M, Gentz R, Parmelee D, Li Y, Galperina O, Giri J, Roschke V, Nardelli B, Carrell J, Sosnovtseva S, Greenfield W, Ruben SM, Olsen HS, Fikes J, Hilbert DM. BLyS: member of the tumor necrosis factor family and B lymphocyte stimulator. Science. 1999;285:260–263. - PubMed
-
- Schneider P, MacKay F, Steiner V, Hofmann K, Bodmer JL, Holler N, Ambrose C, Lawton P, Bixler S, Acha-Orbea H, Valmori D, Romero P, Werner-Favre C, Zubler RH, Browning JL, Tschopp J. BAFF, a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor family, stimulates B cell growth. J Exp Med. 1999;189:1747–1756. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

