Leiomodin is an actin filament nucleator in muscle cells
- PMID: 18403713
- PMCID: PMC2845909
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1155313
Leiomodin is an actin filament nucleator in muscle cells
Abstract
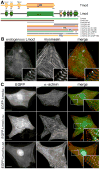
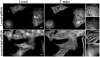
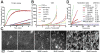
Initiation of actin polymerization in cells requires nucleation factors. Here we describe an actin-binding protein, leiomodin, that acted as a strong filament nucleator in muscle cells. Leiomodin shared two actin-binding sites with the filament pointed end-capping protein tropomodulin: a flexible N-terminal region and a leucine-rich repeat domain. Leiomodin also contained a C-terminal extension of 150 residues. The smallest fragment with strong nucleation activity included the leucine-rich repeat and C-terminal extension. The N-terminal region enhanced the nucleation activity threefold and recruited tropomyosin, which weakly stimulated nucleation and mediated localization of leiomodin to the middle of muscle sarcomeres. Knocking down leiomodin severely compromised sarcomere assembly in cultured muscle cells, which suggests a role for leiomodin in the nucleation of tropomyosin-decorated filaments in muscles.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

