Deconstruction of iterative multidomain polyketide synthase function
- PMID: 18403714
- PMCID: PMC2480491
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1154711
Deconstruction of iterative multidomain polyketide synthase function
Abstract
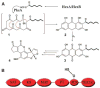
PksA, which initiates biosynthesis of the environmental carcinogen aflatoxin B1, is one of the multidomain iterative polyketide synthases (IPKSs), a large, poorly understood family of biosynthetic enzymes. We found that dissection of PksA and its reconstitution from selected sets of domains allows the accumulation and characterization of advanced octaketide intermediates bound to the enzyme, permitting the reactions controlled by individual catalytic domains to be identified. A product template (PT) domain unites with the ketosynthase and thioesterase in this IPKS system to assemble precisely seven malonyl-derived building blocks to a hexanoyl starter unit and mediate a specific cyclization cascade. Because the PT domain is common among nonreducing IPKSs, these mechanistic features should prove to be general for IPKS-catalyzed production of aromatic polyketides.
Figures


Comment in
-
Biochemistry. Anatomy of a fungal polyketide synthase.Science. 2008 Apr 11;320(5873):186-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1157677. Science. 2008. PMID: 18403699 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

