The TWEAK-Fn14 cytokine-receptor axis: discovery, biology and therapeutic targeting
- PMID: 18404150
- PMCID: PMC3018765
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd2488
The TWEAK-Fn14 cytokine-receptor axis: discovery, biology and therapeutic targeting
Abstract
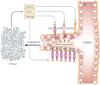
TWEAK is a multifunctional cytokine that controls many cellular activities including proliferation, migration, differentiation, apoptosis, angiogenesis and inflammation. TWEAK acts by binding to Fn14, a highly inducible cell-surface receptor that is linked to several intracellular signalling pathways, including the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) pathway. The TWEAK-Fn14 axis normally regulates various physiological processes, in particular it seems to play an important, beneficial role in tissue repair following acute injury. Furthermore, recent studies have indicated that TWEAK-Fn14 axis signalling may contribute to cancer, chronic autoimmune diseases and acute ischaemic stroke. This Review provides an overview of TWEAK-Fn14 axis biology and summarizes the available data supporting the proposal that both TWEAK and Fn14 should be considered as potential targets for the development of novel therapeutics.
Figures

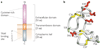




References
-
- Foster D, Parrish-Novak J, Fox B, Xu W. Cytokine–receptor pairing: accelerating discovery of cytokine function. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 2004;3:160–170. - PubMed
-
- Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell. 2001;104:487–501. - PubMed
-
- Bodmer J, Schneider P, Tschopp J. The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002;27:19–26. - PubMed
-
-
Chicheportiche Y, et al. TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:32401–32410. References 4 and 5 describe the initial cloning and characterization of the TWEAK cytokine.
-
-
- Marsters SA, et al. Identification of a ligand for the death-domain-containing receptor Apo3. Curr. Biol. 1998;8:525–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

