Adenosine 5'-triphosphate and its relationship with other mediators that activate pelvic nerve afferent neurons in the rat colorectum
- PMID: 18404489
- PMCID: PMC2104004
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-005-5305-2
Adenosine 5'-triphosphate and its relationship with other mediators that activate pelvic nerve afferent neurons in the rat colorectum
Abstract
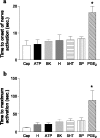
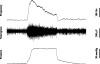
Evidence of a role for purinergic signalling in visceral afferents involving P2X(2), P2X(3) and P2Y(1) receptors exists, which appears to be important during inflammation. This study aimed to evaluate the degree of interaction between adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) and other mediators that activate sensory nerves in the colorectum. Recordings from pelvic nerve afferents were made during application of agents to the in-vitro colorectal preparation. Analysis allowed calculation of single unit activity. When applied individually, bradykinin (78%) and 5-hydoxytryptamine (77%) activated the greatest number of neurons, followed by substance P, protons, ATP and capsaicin. Prostaglandin E(2) stimulated the least number (54%) and had a longer latency. Seventy-seven percent of all units studied either responded to both ATP and capsaicin or to neither, giving the greatest degree of activity correlation. Five percent of units were activated by all seven agents and no units were activated by a single agent alone. 5-hydroxytryptamine, capsaicin and protons, when co-applied with ATP, increased pelvic nerve activity to a greater degree than the sum of the individual responses. It is concluded that ATP activates pelvic nerve afferents and acts synergistically with protons, capsaicin and 5-hydroxytryptamine. The pattern of neuronal activation suggests that visceral afferents are polymodal but the receptor expression on their terminals is variable.
Figures





References
-
- Burnstock G. P2X receptors in sensory neurones. Br J Anaesth 2000; 84: 476–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

