Guanosine stimulates neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells via activation of heme oxygenase and cyclic GMP
- PMID: 18404501
- PMCID: PMC2096532
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-005-6214-0
Guanosine stimulates neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells via activation of heme oxygenase and cyclic GMP
Abstract
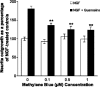
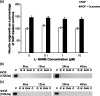
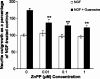
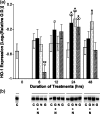
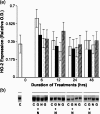
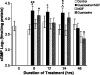
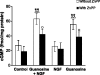
Undifferentiated rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells extend neurites when cultured in the presence of nerve growth factor (NGF). Extracellular guanosine synergistically enhances NGF-dependent neurite outgrowth. We investigated the mechanism by which guanosine enhances NGF-dependent neurite outgrowth. Guanosine administration to PC12 cells significantly increased guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) within the first 24 h whereas addition of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) inhibitors abolished guanosine-induced enhancement of NGF-dependent neurite outgrowth. sGC may be activated either by nitric oxide (NO) or by carbon monoxide (CO). [Formula: see text]-Nitro-L-: arginine methyl ester (L-: NAME), a non-isozyme selective inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), had no effect on neurite outgrowth induced by guanosine. Neither nNOS (the constitutive isoform), nor iNOS (the inducible isoform) were expressed in undifferentiated PC12 cells, or under these treatment conditions. These data imply that NO does not mediate the neuritogenic effect of guanosine. Zinc protoporphyrin-IX, an inhibitor of heme oxygenase (HO), reduced guanosine-dependent neurite outgrowth but did not attenuate the effect of NGF. The addition of guanosine plus NGF significantly increased the expression of HO-1, the inducible isozyme of HO, after 12 h. These data demonstrate that guanosine enhances NGF-dependent neurite outgrowth by first activating the constitutive isozyme HO-2, and then by inducing the expression of HO-1, the enzymes responsible for CO synthesis, thus stimulating sGC and increasing intracellular cGMP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide donors enhance neurotrophin-induced neurite outgrowth through a cGMP-dependent mechanism.J Neurosci Res. 1997 Feb 15;47(4):427-39. J Neurosci Res. 1997. PMID: 9057136
-
Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade through nitric oxide synthesis as a mechanism of neuritogenic effect of genipin in PC12h cells.J Neurochem. 2001 Oct;79(1):45-54. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00533.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11595756
-
Both neuronal NO synthase and nitric oxide are required for PC12 cell differentiation: a cGMP independent pathway.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999 Feb 5;64(2):165-78. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(98)00315-5. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 9931481
-
GTP and guanosine synergistically enhance NGF-induced neurite outgrowth from PC12 cells.Int J Dev Neurosci. 1996 Feb;14(1):19-34. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(95)00083-6. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8779305
-
Formation, signaling functions, and metabolisms of nitrated cyclic nucleotide.Nitric Oxide. 2013 Nov 1;34:10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Nitric Oxide. 2013. PMID: 23632125 Review.
Cited by
-
The Guanine-Based Purinergic System: The Tale of An Orphan Neuromodulation.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Jun 17;7:158. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00158. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27378923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guanosine: a Neuromodulator with Therapeutic Potential in Brain Disorders.Aging Dis. 2016 Oct 1;7(5):657-679. doi: 10.14336/AD.2016.0208. eCollection 2016 Oct. Aging Dis. 2016. PMID: 27699087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guanosine inhibits LPS-induced pro-inflammatory response and oxidative stress in hippocampal astrocytes through the heme oxygenase-1 pathway.Purinergic Signal. 2015 Dec;11(4):571-80. doi: 10.1007/s11302-015-9475-2. Epub 2015 Oct 2. Purinergic Signal. 2015. PMID: 26431832 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Role of Guanosine on Human Neuroblastoma Cell Differentiation and the Underlying Molecular Mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 27;12:658806. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.658806. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33986683 Free PMC article.
-
Unfolding New Roles for Guanine-Based Purines and Their Metabolizing Enzymes in Cancer and Aging Disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 16;12:653549. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.653549. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33935764 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/ddr.430280303', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.430280303'}]}
- Burnstock G. Physiological and pathological roles of purines: An update. Drug Dev Res 1993; 28: 195–206.
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0166-2236(96)81861-3', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-2236(96)81861-3'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8787135', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8787135/'}]}
- Neary JT, Rathbone MP, Cattabeni F et al. Trophic actions of extracellular nucleotides and nucleosides on glial and neuronal cells. Trends Neurosci 1996; 19: 13-. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0301-0082(99)00017-9', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-0082(99)00017-9'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10845757', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10845757/'}]}
- Rathbone MP, Middlemiss PJ, Gysbers JW et al. Trophic effects of purines in neurons and glial cells. Prog Neurobiol 1999; 59: 663-0. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1006/bbrc.1995.2215', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1995.2215'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7654253', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7654253/'}]}
- Abbracchio MP, Ceruti S, Barbieri D et al. A novel action for adenosine: Apoptosis of astroglial cells in rat brain primary cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1995; 213: 908-5. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/ddr.1128', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.1128'}]}
- Di Iorio P, Caciagli F, Giuliani P et al. Purine nucleosides protect injured neurons and stimulate neuronal regeneration by intracellular and membrane receptor-mediated mechanisms. Drug Dev Res 2001; 52: 303-5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

