Visualizing new dimensions in Drosophila myoblast fusion
- PMID: 18404690
- PMCID: PMC2664634
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.20756
Visualizing new dimensions in Drosophila myoblast fusion
Abstract
Over several years, genetic studies in the model system, Drosophila melanogastor, have uncovered genes that when mutated, lead to a block in myoblast fusion. Analyses of these gene products have suggested that Arp2/3-mediated regulation of the actin cytoskeleton is crucial to myoblast fusion in the fly. Recent advances in imaging in Drosophila embryos, both in fixed and live preparations, have led to a new appreciation of both the three-dimensional organization of the somatic mesoderm and the cell biology underlying myoblast fusion.
(c) 2008 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
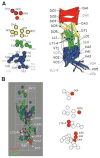
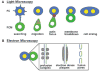

References
-
- Patel K, Christ B, Stockdale FE. Control of muscle size during embryonic, fetal, and adult life. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002;38:163–186. - PubMed
-
- Abmayr SM, Balagopalan L, Galletta BJ, Hong SJ. Cell and molecular biology of myoblast fusion. Int Rev Cytol. 2003;225:33–89. - PubMed
-
- Horsley V, Pavlath GK. Forming a multinucleated cell: molecules that regulate myoblast fusion. Cells Tissues Organs. 2004;176:67–78. - PubMed
-
- Bate M. The embryonic development of larval muscles in Drosophila. Development. 1990;110:791–804. - PubMed
-
- Baylies MK, Bate M, Ruiz Gomez M. Myogenesis: a view from Drosophila. Cell. 1998;93:921–927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

