Involvement of connexin 43 in angiotensin II-induced migration and proliferation of saphenous vein smooth muscle cells via the MAPK-AP-1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 18405916
- PMCID: PMC2765202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.03.002
Involvement of connexin 43 in angiotensin II-induced migration and proliferation of saphenous vein smooth muscle cells via the MAPK-AP-1 signaling pathway
Abstract
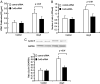
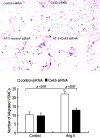
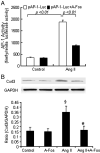
Proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) lead to intimal thickening and influence the long-term patency of venous graft post coronary arterial bypass graft. There is increasing evidence that connexins are involved in the development of intimal hyperplasia and restenosis. We assessed connexin 43 (Cx43) expression and its role in angiotensin II-induced proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells and the signal pathways involved in human saphenous vein bypass conduits. Angiotensin II significantly increased gap junctional intercellular communication and induced the expression of Cx43 in human saphenous vein SMCs in a dose- and time-dependent manner through angiotensin II type 1 receptor. The effect of angiotensin II was blocked by siRNA of ERK 1/2, p38 MAPK and JNK, respectively. Overexpression of Cx43 markedly increased the proliferation of saphenous vein SMCs. However, siRNA for Cx43 inhibited angiotensin II-induced proliferation, cyclin E expression and migration of human saphenous vein SMCs. In dual-luciferase reporter assay, angiotensin II markedly activated AP-1 transcription factor, which was significantly attenuated by a dominant-negative AP-1 (A-Fos) with subsequent inhibition of angiotensin II-induced transcriptional expression of Cx43. These data demonstrate the role of Cx43 in the proliferation and migration of human saphenous vein SMCs and angiotensin II-induced Cx43 expression via mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK)-AP-1 signaling pathway.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between angiotensin II and IGF-1-induced connexin 43 expression in human saphenous vein smooth muscle cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2011 Aug;15(8):1695-702. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01161.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 20731749 Free PMC article.
-
Breviscapine inhibits high glucose-induced proliferation and migration of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells of rats via suppressing the ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 May;33(5):606-14. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.6. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22465949 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in smooth muscle cells by angiotensin II: involvement of p22phox and reactive oxygen species.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000 Apr;20(4):940-8. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.20.4.940. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000. PMID: 10764657
-
Angiotensin II enhances AT1-Nox1 binding and stimulates arterial smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation through AT1, Nox1, and interleukin-18.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Aug 1;303(3):H282-96. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00231.2012. Epub 2012 May 25. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22636674 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of the Proinflammatory IL-6-JAK/STAT Signalling Pathways Responsible for Vascular Restenosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Cardiol Res Pract. 2019 Jan 2;2019:9846312. doi: 10.1155/2019/9846312. eCollection 2019. Cardiol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 30719343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of Telmisartan on the expression of connexin43 and neointimal hyperplasia in a rabbit iliac artery restenosis model.Heart Vessels. 2019 Jul;34(7):1230-1239. doi: 10.1007/s00380-018-01338-1. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Heart Vessels. 2019. PMID: 30671641
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces phosphorylation of PI3K-Akt/PKB to potentiate proliferation of smooth muscle cells in human saphenous vein.Exp Mol Pathol. 2010 Aug;89(1):20-6. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.04.002. Epub 2010 May 13. Exp Mol Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20471974 Free PMC article.
-
CX43 change in LPS preconditioning against apoptosis of mesenchymal stem cells induced by hypoxia and serum deprivation is associated with ERK signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Aug;380(1-2):267-75. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1683-x. Epub 2013 May 28. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23712704
-
Upregulation of connexin43 by glucose deprivation in H9c2 cells via the extracellular signal‑regulated kinase/mitogen‑activated protein kinase signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jan;17(1):729-734. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7967. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29115504 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin 43 plays a role in proliferation and migration of pulmonary arterial fibroblasts in response to hypoxia.Pulm Circ. 2020 Jul 6;10(3):2045894020937134. doi: 10.1177/2045894020937134. eCollection 2020 Jul-Sep. Pulm Circ. 2020. PMID: 32670564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deglise S, Martin D, Probst H, Saucy F, Hayoz D, Waeber G, et al. Increased connexin43 expression in human saphenous veins in culture is associated with intimal hyperplasia. J Vasc Surg. 2005;41:1043–52. - PubMed
-
- Jia G, Mitra AK, Cheng G, Gangahar DM, Agrawal DK. Angiotensin II and IGF-1 regulate connexin43 expression via ERK and p38 signaling pathways in vascular smooth muscle cells of coronary artery bypass conduits. J Surg Res. 2007;142:137–42. - PubMed
-
- Jia G, Cheng G, Agrawal DK. Differential effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 and atheroma-associated cytokines on cell proliferation and apoptosis in plaque smooth muscle cells of symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with carotid stenosis. Immunol Cell Biol. 2006;84:422–9. - PubMed
-
- Jia G, Cheng G, Agrawal DK. Autophagy of vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerotic lesions. Autophagy. 2007;3:63–4. - PubMed
-
- Kwak BR, Mulhaupt F, Veillard N, Gros DB, Mach F. Altered pattern of vascular connexin expression in atherosclerotic plaques. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:225–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

