Reactive oxygen species and angiogenesis: NADPH oxidase as target for cancer therapy
- PMID: 18406051
- PMCID: PMC2673114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.02.044
Reactive oxygen species and angiogenesis: NADPH oxidase as target for cancer therapy
Abstract
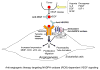
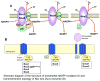
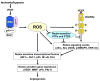
Angiogenesis is essential for tumor growth, metastasis, arteriosclerosis as well as embryonic development and wound healing. Its process is dependent on cell proliferation, migration and capillary tube formation in endothelia cells (ECs). High levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as superoxide and H2O2 are observed in various cancer cells. Accumulating evidence suggests that ROS function as signaling molecules to mediate various growth-related responses including angiogenesis. ROS-dependent angiogenesis can be regulated by endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as SOD and thioredoxin. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), one of the major angiogenesis factor, is induced in growing tumors and stimulates EC proliferation and migration primarily through the VEGF receptor type2 (VEGFR2, Flk1/KDR). Major source of ROS in ECs is a NADPH oxidase which consists of Nox1, Nox2, Nox4, Nox5, p22phox, p47phox and the small G-protein Rac1. NADPH oxidase is activated by various growth factors including VEGF and angiopoietin-1 as well as hypoxia and ischemia, and ROS derived from this oxidase are involved in VEGFR2 autophosphorylation, and diverse redox signaling pathways leading to induction of transcription factors and genes involved in angiogenesis. Dietary antioxidants appear to be effective for treatment of tumor angiogenesis. The aim of this review is to provide an overview of the recent progress on role of ROS derived from NADPH oxidase and redox signaling events involved in angiogenesis. Understanding these mechanisms may provide insight into the NADPH oxidase and redox signaling components as potential therapeutic targets for tumor angiogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1995;1(1):27–31. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov 18;285(21):1182–1186. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Davis-Smyth T. The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev. 1997;18(1):4–25. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto T, Claesson-Welsh L. VEGF receptor signal transduction. Sci STKE. 2001 Dec 11;2001(112):RE21. - PubMed
-
- Lyden D, Hattori K, Dias S, Costa C, Blaikie P, Butros L, Chadburn A, Heissig B, Marks W, Witte L, Wu Y, Hicklin D, Zhu Z, Hackett NR, Crystal RG, Moore MA, Hajjar KA, Manova K, Benezra R, Rafii S. Impaired recruitment of bone-marrow-derived endothelial and hematopoietic precursor cells blocks tumor angiogenesis and growth. Nat Med. 2001 Nov;7(11):1194–1201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

