Characterization of protein factor(s) in rat bronchoalveolar lavage fluid that enhance insulin transport via transcytosis across primary rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers
- PMID: 18406118
- PMCID: PMC3638983
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.01.028
Characterization of protein factor(s) in rat bronchoalveolar lavage fluid that enhance insulin transport via transcytosis across primary rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers
Abstract
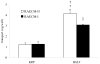
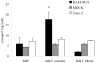
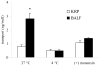
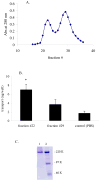
The aim of this study was to characterize factor(s) in rat bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) that enhance(s) insulin transport across primary rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers (RAECM) in primary culture. BALF was concentrated 7.5-fold using the Centricon device and the retentate was used to characterize the factor(s) involved in enhancing apical-to-basolateral transport of intact 125I-insulin across various epithelial cell monolayers. These factor(s) enhanced transport of intact insulin across type II cell-like RAECM (3-fold increase) and type I cell-like RAECM (2-fold increase), but not across Caco-2 or MDCK cell monolayers. The insulin transport-enhancing factor(s) were temperature- and trypsin-sensitive. The mechanism of enhancement did not seem to involve paracellular transport or fluid-phase endocytosis, since fluxes of sodium fluorescein and FITC-dextran (70 kDa) were not affected by the factor(s) in the apical bathing fluid. BALF enhancement of intact 125I-insulin transport was abolished at 4 degrees C and in the presence of monensin, suggesting involvement of transcellular pathways. Sephacryl S-200 purification of BALF retentate, followed by LC-MS/MS, indicated that the high molecular weight (>100 kDa) fractions (which show some homology to alpha-1-inhibitor III, murinoglobulin gamma 2, and pregnancy-zone protein) appear to facilitate transcellular transport of insulin across RAECM.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhancement of insulin transport across primary rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers by endogenous cellular factor(s).Pharm Res. 2007 Sep;24(9):1713-9. doi: 10.1007/s11095-007-9301-9. Epub 2007 Apr 19. Pharm Res. 2007. PMID: 17443400
-
Transcytosis of GCSF-transferrin across rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers.Pharm Res. 2003 Aug;20(8):1231-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1025005232421. Pharm Res. 2003. PMID: 12948021
-
Translocation of PEGylated quantum dots across rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers.Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:2849-57. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S26051. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011. PMID: 22131830 Free PMC article.
-
Size-dependent dextran transport across rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers.J Pharm Sci. 1997 Mar;86(3):305-9. doi: 10.1021/js960352x. J Pharm Sci. 1997. PMID: 9050797
-
Receptor-mediated endocytosis of macromolecules and strategy to enhance their transport in alveolar epithelial cells.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 May;12(5):813-25. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2015.992778. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25496474 Review.
Cited by
-
Conjugation with cationic cell-penetrating peptide increases pulmonary absorption of insulin.Mol Pharm. 2009 Mar-Apr;6(2):492-503. doi: 10.1021/mp800174g. Mol Pharm. 2009. PMID: 19228019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patton JS, Byron PR. Inhaling medicines: delivering drugs to the body through the lungs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Patton JS. Mechanisms of macromolecule absorption by the lungs. Adv Drug Del Rev. 1996;19:3–36.
-
- Wattiez R, Falmagne P. Proteomics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005;815:169–178. - PubMed
-
- Wattiez R, Hermans C, Bernard A, Lesur O, Falmagne P. Human bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, amino acid microsequencing and identification of major proteins. Electrophoresis. 1999;20:1634–1645. - PubMed
-
- Hastings RH, Folkesson HG, Matthay MA. Mechanisms of alveolar protein clearance in the intact lung. Am J Physiol. 2004;286:679–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

