A stable isotope breath test with a standard meal for abnormal gastric emptying of solids in the clinic and in research
- PMID: 18406670
- PMCID: PMC3739971
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2008.01.009
A stable isotope breath test with a standard meal for abnormal gastric emptying of solids in the clinic and in research
Abstract
Background & aims: The aim of this study was to validate a [13C]-Spirulina platensis gastric emptying (GE) breath test (GEBT) with a standardized meal.
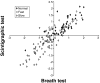
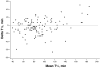
Methods: Thirty-eight healthy volunteers and 129 patients with clinically suspected delayed GE underwent measurements at 45, 90, 120, 150, 180, and 240 minutes after a 238 kcal meal labeled test with 100 mg [13C]-S platensis and 0.5 mCi 99mTc. We established normal ranges for scintigraphy with this test meal, intraindividual and interindividual coefficients of variation (COVs), and the ability of the [13C] GEBT breath percent dose excreted *1000 values to predict scintigraphic half-life and to categorize GE as delayed, normal, or accelerated.
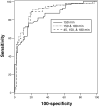
Results: In health, the 10th and 90th percentiles of half-life for scintigraphic GE with this meal were 52 and 86 minutes; intraindividual COVs for scintigraphy and the GEBT were, respectively, 31% and 27% at 45 minutes, 17% and 21% at 90 minutes, 13% and 16% at 120 minutes, 10% and 13% at 150 minutes, and 8% and 12% at 180 minutes. Interindividual COVs at each time for the [13C] GEBT and scintigraphy were typically approximately 1%-4% lower than intraindividual COVs. Individual breath samples at 45, 150, and 180 minutes predicted GE category; at 80% specificity, 45- and 180-minute samples combined were 93% sensitive to identify accelerated GE, and 150- and 180-minute combined were 89% sensitive for delayed GE.
Conclusions: [13C]-S platensis GEBT is as reproducible as scintigraphy; imprecision with both tests reflects physiologic variation. With 4 breath samples, this method with an off-the-shelf meal is valid to assess GE in clinic and in research.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest exist for all of the authors.
Figures



References
-
- Ghoos YF, Maes BD, Geypens BJ, Mys G, Hiele MI, Rutgeerts PJ, Vantrappen G. Measurement of gastric emptying rate of solids by means of a carbon-labeled octanoic acid breath test. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:1640–1647. - PubMed
-
- Choi M-G, Camilleri M, Burton DD, Zinsmeister AR, Forstrom LA, Nair KS. 13C-octanoic acid breath test for gastric emptying of solids: accuracy, reproducibility and comparison with scintigraphy. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:1155–1162. - PubMed
-
- Choi M-G, Camilleri M, Burton DD, Zinsmeister AR, Forstrom LA, Nair KS. Reproducibility and simplification of 13C-octanoic acid breath test for gastric emptying of solids. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:92–98. - PubMed
-
- Lee J-S, Camilleri M, Zinsmeister AR, Burton DD, Choi M-G, Nair KS, Verlinden M. Toward office-based measurement of gastric emptying in symptomatic diabetics using [13C]octanoic acid breath test. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:2751–2761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

